
B09-Magnetism
B10-Static Electricity
Proficiency Standards
B12-Electromagnets
 |
B09-Magnetism |
B10-Static Electricity |
 Proficiency Standards
|
 B12-Electromagnets |
|
Electric Current &
Circuits |
| What is electric current? |
 How do electric charges flow? How do electric charges flow? (Mastery) |
 How do we use electric current? How do we use electric current? (Interpersonal) |
 What types of electronics are there? What types of electronics are there?(Understanding) |
 What can electric current do? What can electric current do?(Self Expressive) |
|
Take every day before sleeping! Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * > 
|
Vocabulary Electric Current & Magnetic Fields Chapter 1, Section3 Pages 30-35 Audiobook Electric Circuit Measurements Chapter 2, Section 2 Pages 56-59 Audiobook Series and Parallel Circuits Chapter 2, Section3 Pages 64-67 Audiobook Investigating Electromagnetism - Worksheet Edison - Worksheet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
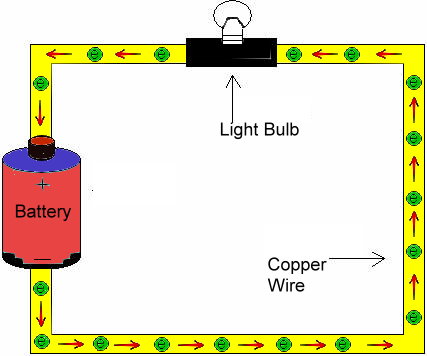 |
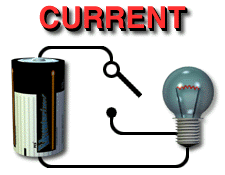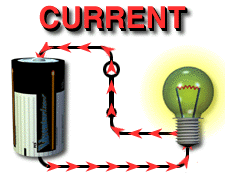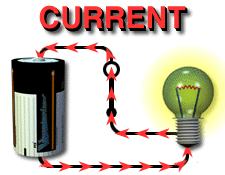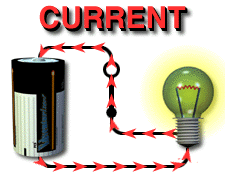
Electric current is the
continuous flow of electrons (note: a spark is not continuous.) The amount of charges per second is measured in amperes (amps or A). |
 |
An
electric
circuit is a closed
(complete) path that allows current to flow. An open circuit (switch is open) stops the flow of electrons. |
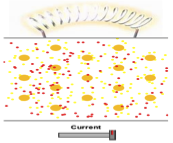 |
A resistor
or semiconductor
is a material like silicon, germanium, or arsenic (used in computer
chips) that lose or use electrical energy, slowing the flow. |
 |
A
device is anything that
uses or resists the flow of electrons. Devices include resistors,
buzzers, and light bulbs. They are represented as resistors in a circuit. |
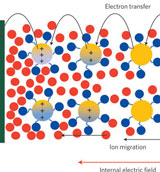 |
Conductors
are materials that allow electrons (red) to flow like metal wires. A
conductor transfers electric charge well, but electric charges do not
flow easily through every material. |
 |
Source: Charges in an electric circuit flow because of a difference in electrical potential energy called voltage, measured in volts (V). You can think of voltage as the amount of force pushing an electric current. A voltage source is a device that creates a potential difference in an electric circuit. |
 |
Resistance
is the measure of how difficult it is for charges to flow through a
material. The greater the resistance, the less current there is for a
given voltage. The unit of measure of resistance is the ohm (Ω). Resistance can vary with:
|
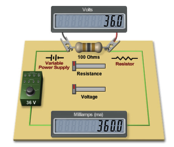 |
 The
relationship between resistance, voltage, and current is summed up in Ohm’s law.
Ohm’s law says that the resistance (R) is equal to the voltage (V)
divided by the current (I). The
relationship between resistance, voltage, and current is summed up in Ohm’s law.
Ohm’s law says that the resistance (R) is equal to the voltage (V)
divided by the current (I). |
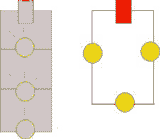 |
If all parts
of an electric circuit are connected one after another along one path,
the circuit is called a series circuit. In a series circuit,
there is only one path for the current to take. Because of this, if one
light goes out in a series circuit, the other lights will go out.
Adding lights to a series circuit will make other lights in the circuit
dimmer. |
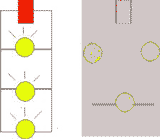 |
In a parallel circuit,
there are several paths (called branches)
for current to take. If one light goes out in a parallel circuit, the
other lights in the circuit will remain lit because there is still
current in the other branches. When branches are added to a parallel
circuit, the overall resistance actually decreases because the current
has more paths to follow. |
 |
A multimeter
includes each of these functions. |
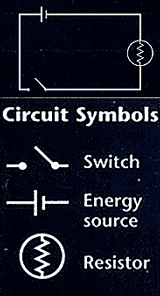 |
A circuit diagram
shows the sources, conductors, and devices (as resistors) using symbols |
 |
Scientist Paul and Joseph Galvin, founders of Schaumburg Illinois based Motorola along with son Paul, developed the car radio and the germanium based transistor in 1955. |
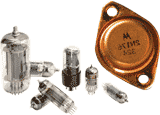 |
Technology The Transistor (1955) was the first mass-produced semiconductor, the forerunner of today's microprocessors at the heart of telephones, TVs, and almost all electronic devices. Transistors allowed early miniaturization of low-power electronics. The older vacuum tubes used to break,burn out, use alot of electricity, and alot of space. |