
 The Science Portal-
The Science Portal-
6th-grade science materials by content sequence.
  The Science Portal- The Science Portal-
6th-grade science materials by content sequence. |
| 2017-2018 Next Generation Science Standards - Phenomenon Bundles (Units) |
|
MMS Workspaces 6th Grade Sites 6th Grade Resources |
Teacher Workspaces Drager McGrath Torgerson |
Essential Knowledge |
NGSS Course 1 Overview NGSS Course 2 Overview |
 Data - SMART Goal |
Scientific Methods |
 Science Process |
 Tech Design |
 Cell Structures MS-LS1-2 |
 Cell Theory MS-LS1-1 |
 Human Body MS-LS1-3 |
|
 Matter MS-PS1-1 |
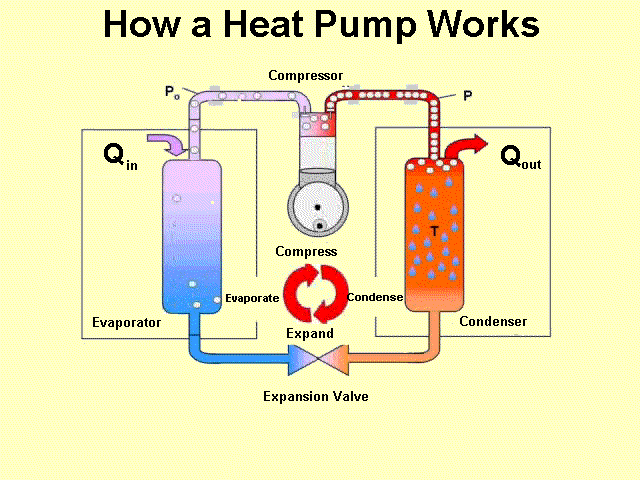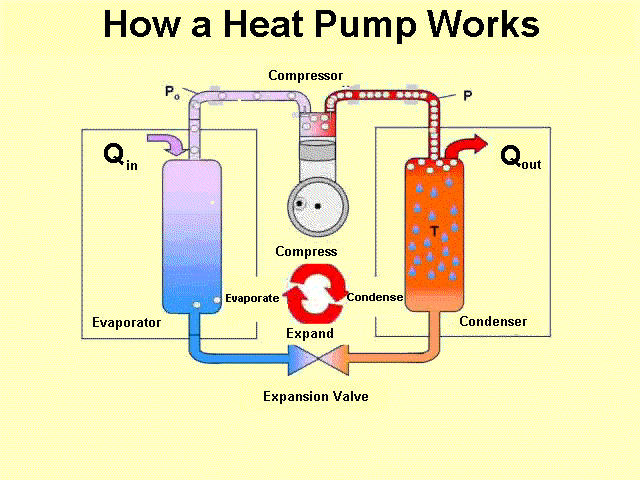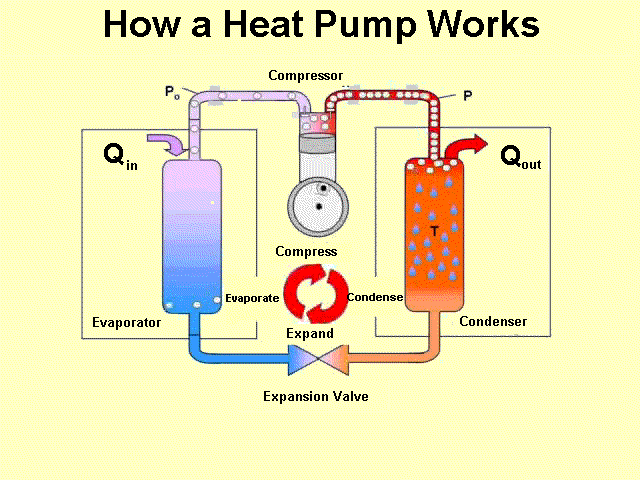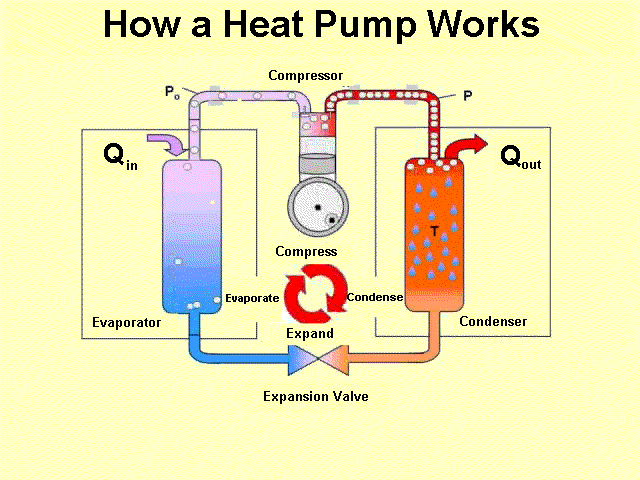
Heat MS-PS1-4 MS-PS3-3 MS-PS3-4 |
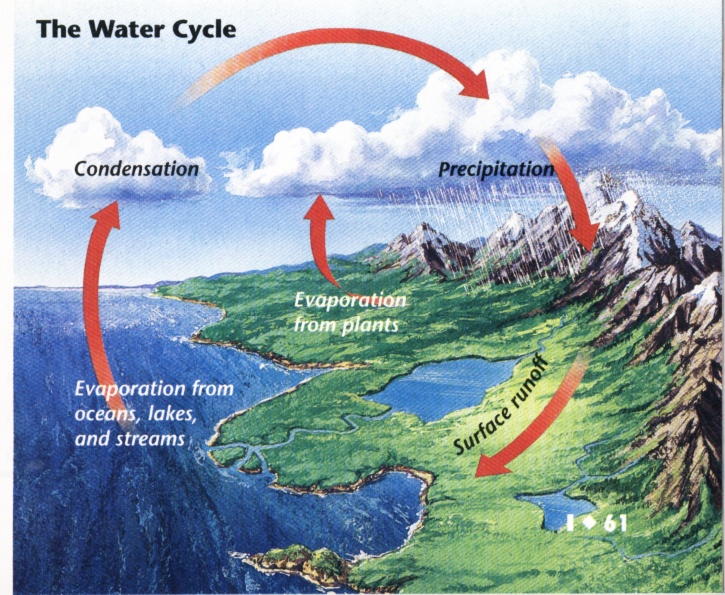 Water Cycle MS-ESS2-4 |
 Weather & Climate MS-ESS2-5 MS-ESS2-6 |
 Ecosystems MS-LS2-1, MS-LS2-2 |
 Plate Tectonics MS-ESS2-2, MS-ESS2-3 |
 Earth's Resources MS-ESS3-1 |
|
 Newton 3 Collisions MS-PS2-1 |
 Newton 1-2 Forces MS-PS2-2 |
 Energy MS-PS3-1 MS-PS3-5 |
 Waves MS-PS4-1 MS-PS4-2 |
 Static & Magnets MS-PS2-5 |
 Electromagnets MS-PS2-3 |
 Gravity MS-PS2-4 |
 Energy MS-PS3-2 |
| GAP Lessons |
 Rock Cycle MS-ESS2-1 |
 Atoms & Elements |
 Pressure |
 Earth, Sun, Moon MS-ESS1-1 |
 Motion |
 Acceleration |
 Sound |
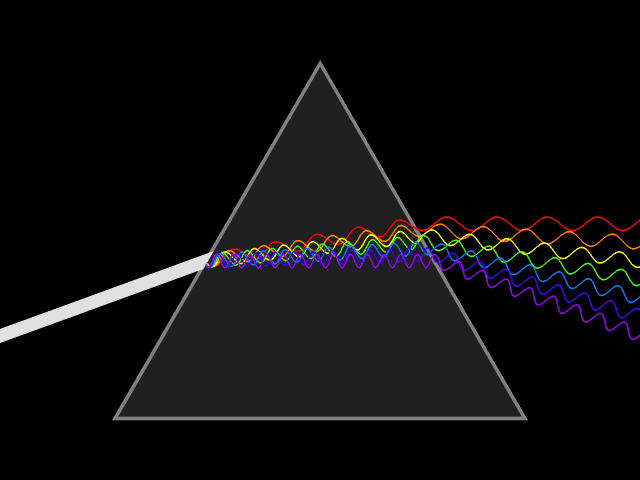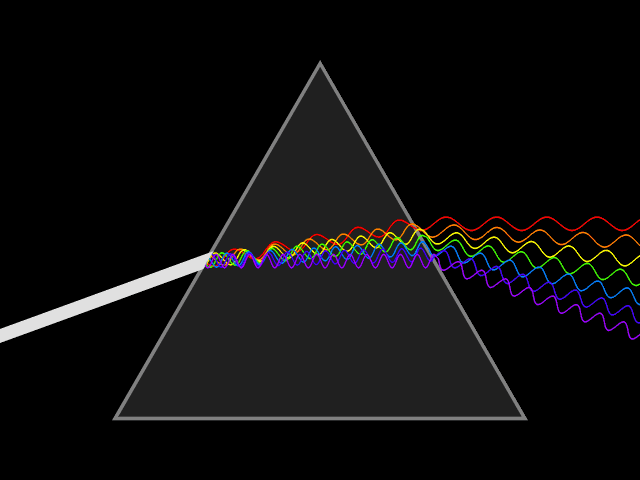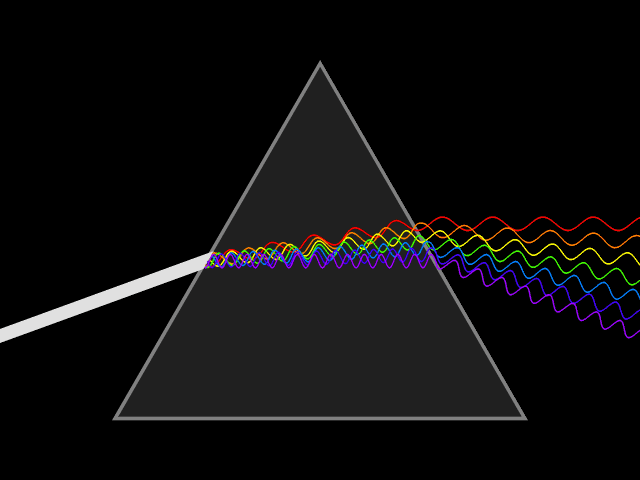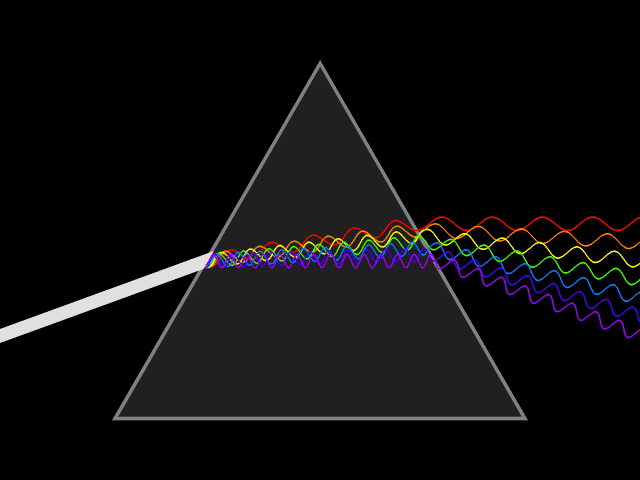 Light |
 Static Electricity MMS-PS2-5 MS-PS2-3 |
 Magnetism MS-PS2-5 MS-PS2-3 |
 Electric Current |
 The Solar System MS-PS2-4 MS-ESS1-2 |
| Enrichment |
 Science News |
 Mechanical Engineering |
 Computer Sciences |
|
 Chemistry |
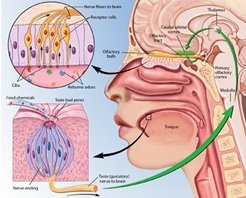 Nervous System MS-LS1-8 |
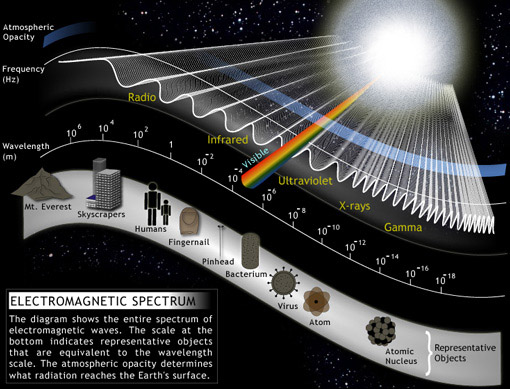 Electromagnetic Waves |
 Aerodynamics- Flight |
| 2017-2018 Next Generation Science Standards - Phenomenon Bundles (Units) |
|
MMS6 Unit 3 Why are bones so hard? Assessments |
MMS6 Unit 2 How does a change in thermal energy affect matter? Assessments |
MMS6 Unit 1 How important are our natural resources? Assessments |
MMS6 Unit 4 What happens when objects collide? Assessments |
MMS6 Unit 5 How can objects interact at a distance? Assessments |
| NGSS Course 2 Bundle 4 | NGSS Course 1 Bundle 2 | NGSS Course 1 Bundle 1 | NGSS Course 1 Bundle 4 | NGSS Course 1 Bundle 5 |
| MS-LS1-2. Develop and use a model to describe the function of a cell as a whole and ways parts of cells contribute to the function. | MS-PS1-1. Develop
models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended
structures. |
MS-LS2-1. Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem. | MS-PS2-1. Apply Newton’s
Third Law to design a solution to a problem involving the motion of two
colliding objects.* |
MS-PS2-3. Ask
questions about data to determine the factors that affect the strength of
electric and magnetic forces. |
| MS-LS1-1. Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that living things are made of cells; either one cell or many different numbers and types of cells. | MS-PS1-4.
Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion,
temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or
removed. |
MS-LS2-2. Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions among organisms across multiple ecosystems. | MS-PS2-2.
Plan an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object’s
motion depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the
object. |
MS-PS2-4. Construct and present arguments using evidence to support
the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the
masses of interacting objects. |
| MS-LS1-3. Use argument
supported by evidence for how the body is a system of interacting
subsystems composed of groups of cells. |
MS-PS3-3. Apply scientific
principles to design, construct, and test a device that either minimizes
or maximizes thermal energy transfer. |
MS-ESS2-2. Construct an explanation based on evidence
for how geoscience processes have changed Earth's surface at varying time
and spatial scales. |
MS-PS3-1.. Construct and
interpret graphical displays of data to describe the relationships of
kinetic energy to the mass of an object and to the speed of an object. |
MS-PS2-5. Conduct an investigation and evaluate the
experimental design to provide evidence that fields exist between objects
exerting forces on each other even though the objects are not in contact. |
| |
MS-PS3-4. Plan an
investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred,
the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic energy
of the particles as measured by the temperature of the sample. |
MS-ESS2-3. Analyze and interpret data on the
distribution of fossils and rocks, continental shapes, and seafloor
structures to provide evidence of the past plate motions. |
MS-PS3-5. Construct, use,
and present arguments to support the claim that when the kinetic energy of
an object changes, energy is transferred to or from the object. |
MS-PS3-2 Develop a model to describe that when the arrangement of objects interacting at a distance changes, different amounts of potential energy are stored in the system |
| |
MS-ESS2-4. Develop a
model to describe the cycling of water through Earth’s systems driven by
energy from the sun and the force of gravity. |
MS-ESS3-1. Construct a
scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distributions
of Earth's mineral, energy, and groundwater resources are the result of
past and current geoscience processes |
MS-PS4-1. Use mathematical
representations to describe a simple model for waves that includes how the
amplitude of a wave is related to the energy in a wave. |
|
| |
MS-ESS2-5. Collect data to
provide evidence for how the motions and complex interactions of air
masses result in changes in weather conditions. |
MS-PS4-2. Develop and use a
model to describe that waves are reflected, absorbed, or transmitted
through various materials. |
||
| |
MS-ESS2-6. Develop and use a
model to describe how unequal heating and rotation of the Earth cause
patterns of atmospheric and oceanic circulation that determine global
climates. |
|||
| |
MS-ETS1-4. Develop a model to generate data for
iterative testing and modification of a proposed object, tool, or process
such that an optimal design can be achieved. |