
Unit 1 Assignments

Ecosystems
MS-LS2-1, MS-LS2-2

Plate Tectonics
MS-ESS2-2, MS-ESS2-3
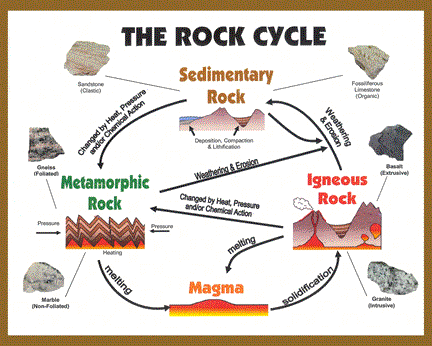
Rock Cycle
MS-ESS2-1
 |
Unit 1 Assignments |
 Ecosystems MS-LS2-1, MS-LS2-2 |
 Plate Tectonics MS-ESS2-2, MS-ESS2-3 |
 Rock Cycle MS-ESS2-1 |
| Natural Resources |
| Bundle 1 How important are our natural resources? |
|
MS-ESS3-1
Evidence Statement Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distributions of Earth's mineral, energy, and groundwater resources are the result of past and current geoscience processes. Packet [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how these resources are limited and typically non-renewable, and how their distributions are significantly changing as a result of removal by humans. Examples of uneven distributions of resources as a result of past processes include but are not limited to petroleum (locations of the burial of organic marine sediments and subsequent geologic traps), metal ores (locations of past volcanic and hydrothermal activity associated with subduction zones), and soil (locations of active weathering and/or deposition of rock).] |
| The concept that
resources are distributed unevenly around the planet as a result of
past geologic processes (ESS3.A as in MS-ESS3-1) connects to the
idea that maps of ancient land and water patterns, based on
investigations of rocks and fossils, make clear how Earth’s plates
have moved great distances, collided, and spread apart (ESS2.B as in
MS-ESS2-3). This concept connects to the idea that humans depend on Earth’s land, ocean, atmosphere, and biosphere for many different resources. Minerals, fresh water, and biosphere resources are limited, and many are not renewable or replaceable over human lifetimes (ESS3.A as in MS-ESS3-1). |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
|
|
|
 |
Plate Tectonics: Earth's crust is divided into parts called plates that float on top of molten rock (mantle) inside Earth.
|
 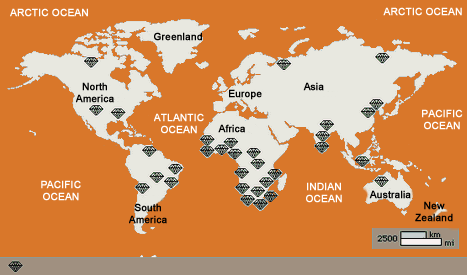 |
Mineral Resources : Mineral
deposits are created in the rock and water cycles and by deposits left by
living things (nitrates, calcium carbonates, etc.)
|
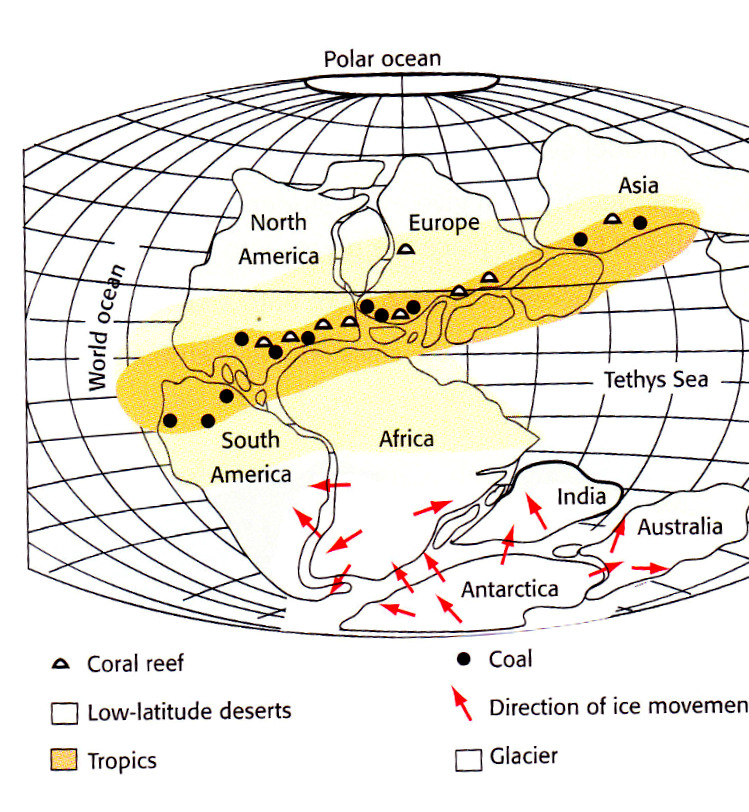 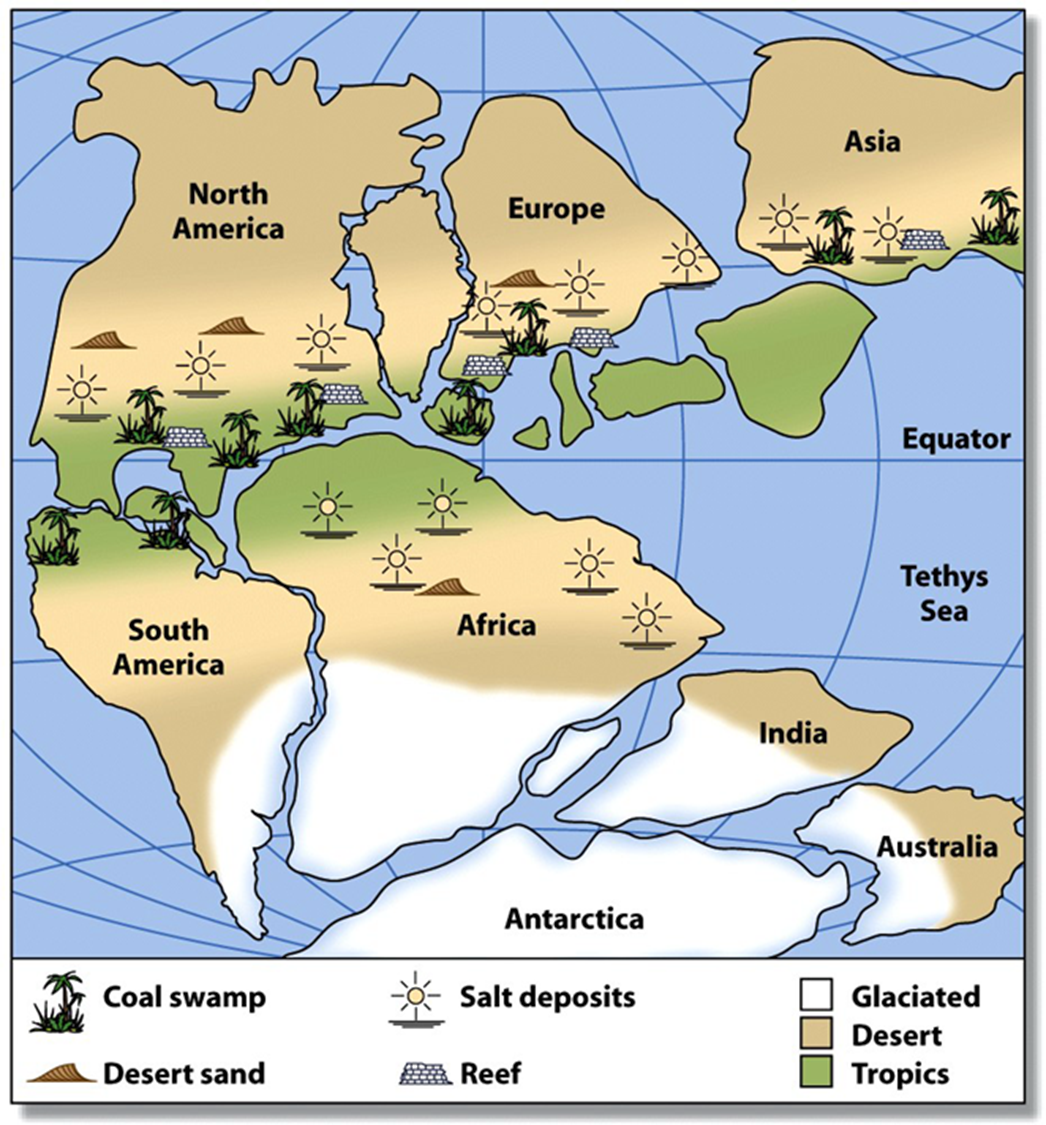 |
Fossil Fuels : were created where enough living things died and became part of the sedimentary and metamorphic rock cycles.
|
Land and Soil Resources: topsoil can be eroded by wind and water or nutrient depletion.
|
|
|
|
Surface Water: Rivers and streams move fresh water,
often depositing it in lakes and ponds.
|
|
|
Groundwater: much of our fresh water supply is stored in the ground and comes to us from wells and springs.
|
| Scientist |
|
| |
Technology |