
Unit 1 Assignments

Ecosystems
MS-LS2-1, MS-LS2-2

Earth's Resources
MS-ESS3-1
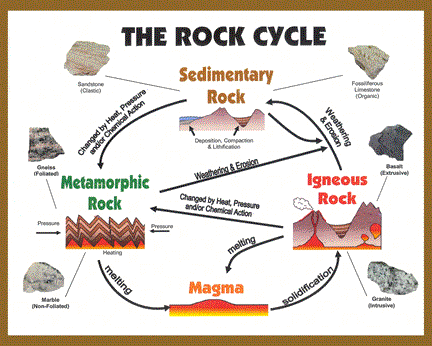
Rock Cycle
MS-ESS2-1
 |
Unit 1 Assignments |
 Ecosystems MS-LS2-1, MS-LS2-2 |
 Earth's Resources MS-ESS3-1 |
 Rock Cycle MS-ESS2-1 |
| Plate Tectonics |
| Bundle 1 How important are our natural resources? |
|
MS-ESS2-2.
Evidence Statement Construct an explanation based on evidence for how geoscience processes have changed Earth's surface at varying time and spatial scales. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how processes change Earth’s surface at time and spatial scales that can be large (such as slow plate motions or the uplift of large mountain ranges) or small (such as rapid landslides or microscopic geochemical reactions), and how many geoscience processes (such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and meteor impacts) usually behave gradually but are punctuated by catastrophic events. Examples of geoscience processes include surface weathering and deposition by the movements of water, ice, and wind. Emphasis is on geoscience processes that shape local geographic features, where appropriate.] MS-ESS2-3. Evidence Statement Analyze and interpret data on the distribution of fossils and rocks, continental shapes, and seafloor structures to provide evidence of the past plate motions. Packet [Clarification Statement: Examples of data include similarities of rock and fossil types on different continents, the shapes of the continents (including continental shelves), and the locations of ocean structures (such as ridges, fracture zones, and trenches).] [Assessment Boundary: Paleomagnetic anomalies in oceanic and continental crust are not assessed.] |
| The concept that
resources are distributed unevenly around the planet as a result of
past geologic processes (ESS3.A as in MS-ESS3-1) connects to the
idea that maps of ancient land and water patterns, based on
investigations of rocks and fossils, make clear how Earth’s plates
have moved great distances, collided, and spread apart (ESS2.B as in
MS-ESS2-3). The idea of geologic processes also connects to the ideas that tectonic processes continually generate new ocean sea floor at ridges and destroy old sea floor at trenches (ESS1.C as in MS-ESS2-3) and that water’s movements—both on the land and underground—cause weathering and erosion, which change the land’s surface features and create underground formations (ESS2.C as in MS-ESS2-2). These concepts connect to the idea that the planet’s systems interact over scales that range from microscopic to global in size, and they operate over fractions of a second to billions of years. These interactions have shaped Earth’s history and will determine its future (ESS2.A as in MS-ESS2-2). |
|
Take every day before sleeping! Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * 
|
Vocabulary - Glossary Drifting Continents - Chapter 1 Section 3: Earth's
Interior
- Chapter 1 Section 1:
Convection Currents and The Mantle
- Chapter 1 Section 2
Booklets and Text Chapters
Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
Plate Tectonics: Earth's crust is divided into parts called plates that float on top of molten rock (mantle) inside Earth.
|
|
Weathering: Surface rock is constantly being broken down by natural forces
such as wind, water, ice, and living things. Erosion: The movement of broken bits of rock by wind, water, and ice with the force of gravity.
|
|
|
|
|
| Scientist |
|
| |
Technology |