
MS-ESS2-1
 |

MS-ESS2-1 |
| Rock Cycle |
|
MS-ESS2-1
Evidence Statement Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
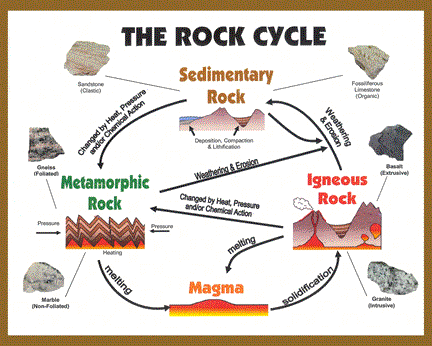
The rock cycle
: Forces inside Earth and at the surface produce a rock cycle that builds,
destroys, and changes the rocks in the crust. Rocks change from one type to another in many possible paths. |
 |
Plate Tectonics: Earth's crust is divided into parts called plates that float on top of molten rock (mantle) inside Earth.
|
|
Weathering: Surface rock is constantly being broken down by natural forces
such as wind, water, ice, and living things. Erosion: The movement of broken bits of rock by wind, water, and ice with the force of gravity.
|
|
|
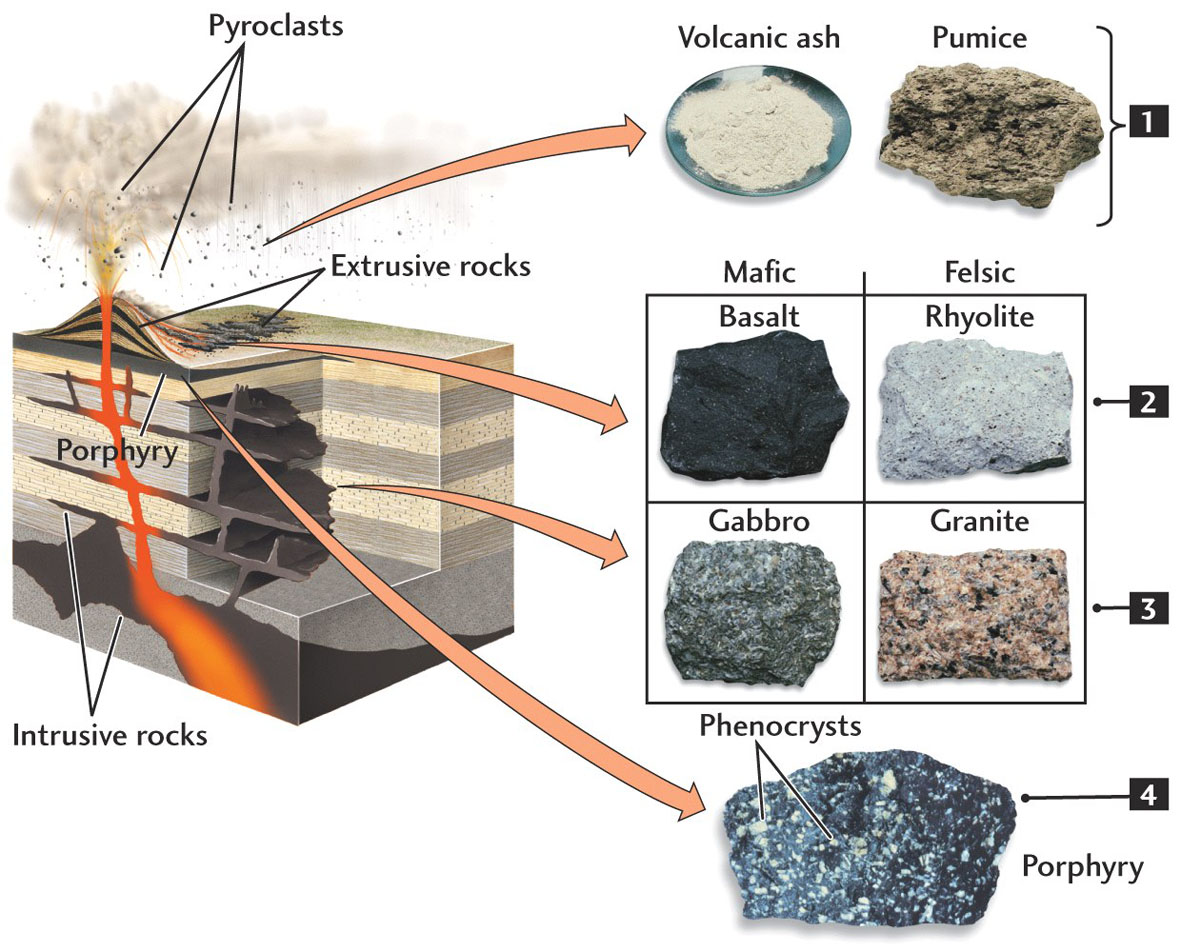
Igneous Rock: is formed from magma
|
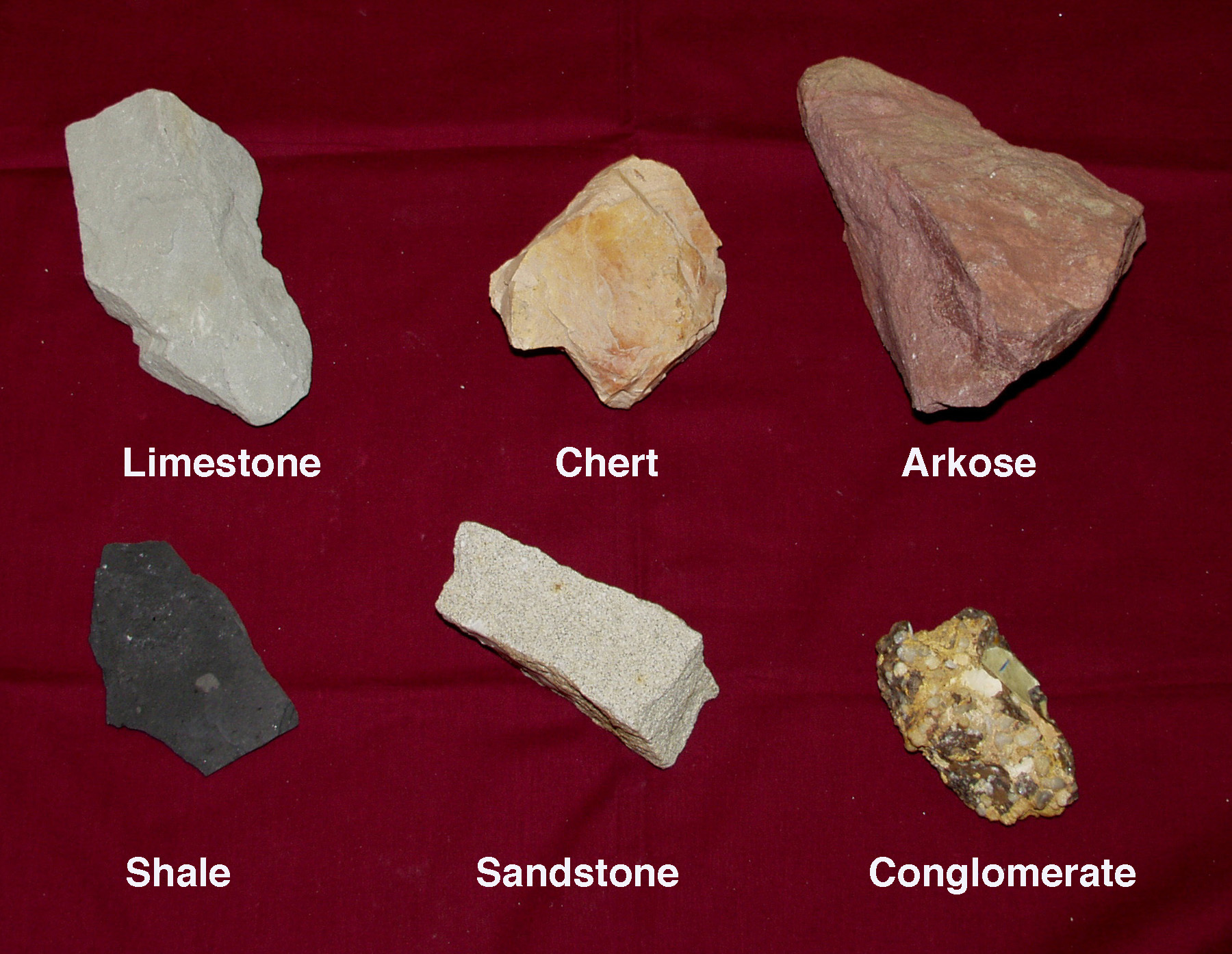 |
Sedimentary Rock: is made from rock particles
(sediment) that are bonded
together to form rock.
|
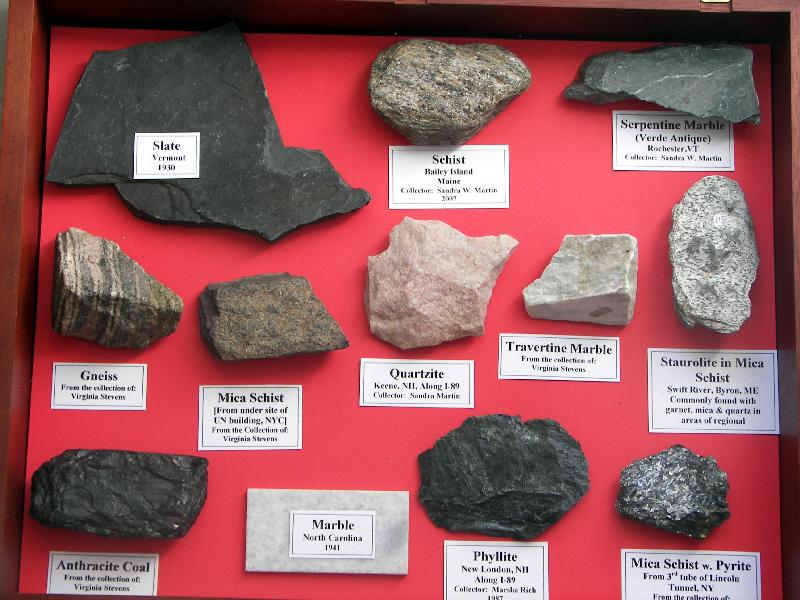 |
Metamorphic Rock: Heat and pressure deep beneath Earth's surface can change any rock into metamorphic rock.
|
| Scientist |
|
| |
Technology |