
Unit 4 Assignments
Newton 3 Collisions
MS-PS2-1

Newton 1-2 Forces
MS-PS2-2

Energy
MS-PS3-1 , MS-PS3-5
B06-Sound
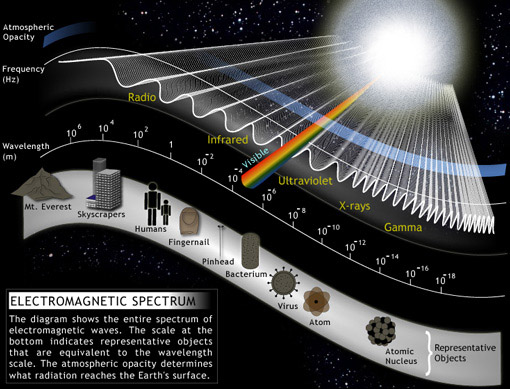
B07-E-M Waves
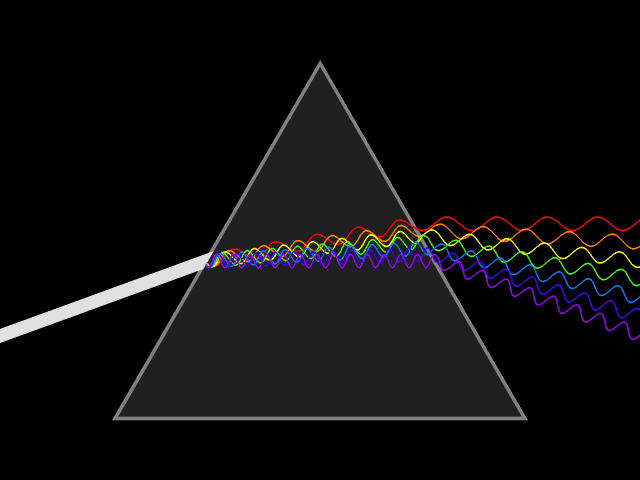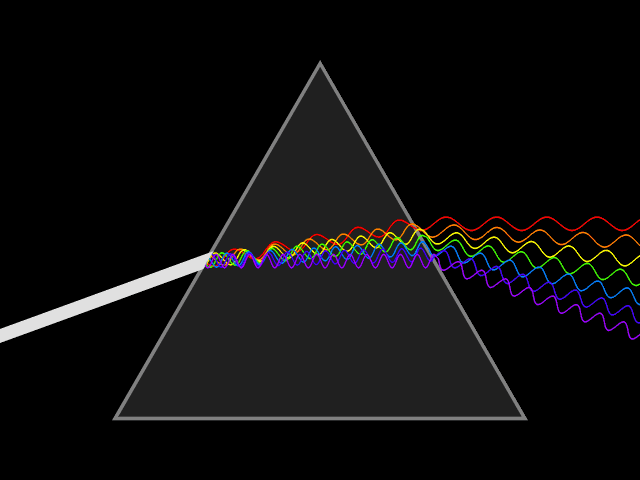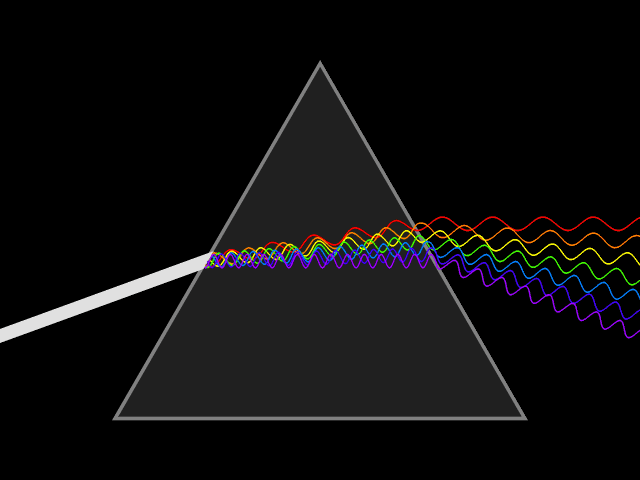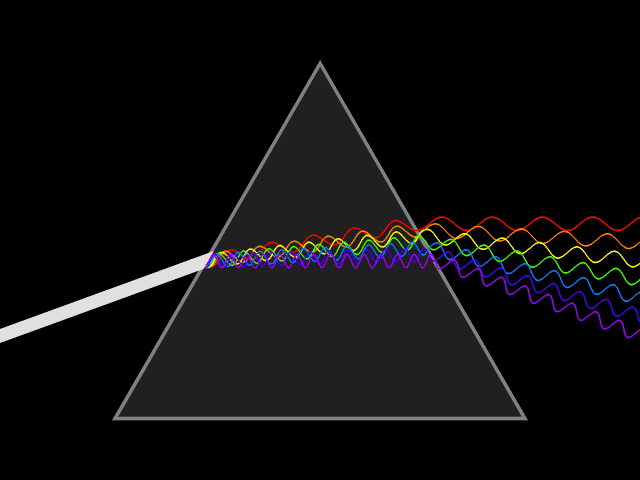
B08-Light
 |
Unit 4 Assignments |
Newton 3 Collisions MS-PS2-1 |
 Newton 1-2 Forces MS-PS2-2 |
 Energy MS-PS3-1 , MS-PS3-5 |
|
Gap Lessons --> |
 B06-Sound |
 B07-E-M Waves |
 B08-Light |
| Waves |
| Bundle 4 What happens when objects collide? |
| MS-PS4-1.
Evidence Statement Use mathematical representations to describe a simple model for waves that includes how the amplitude of a wave is related to the energy in a wave. Packet [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on describing waves with both qualitative and quantitative thinking.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include electromagnetic waves and is limited to standard repeating waves.] |
| MS-PS4-2.
Evidence Statement Develop and use a model to describe that waves are reflected, absorbed, or transmitted through various materials. Packet [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on both light and mechanical waves. Examples of models could include drawings, simulations, and written descriptions.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to qualitative applications pertaining to light and mechanical waves.] |
| Concepts of force and motion also can connect to the ideas that a sound wave needs a medium through which it is transmitted (PS4.A as in MS-PS4-2), and the concept of sound waves connects to the idea that a simple wave has a repeating pattern with a specific wavelength, frequency, and amplitude (PS4.Aas in MS-PS4-1). Finally, the concepts of waves connect to the idea of a wave model of light, and the idea that this wave model is useful for explaining brightness, color, and the frequency-dependent bending of light at a surface between media (PS4.B as in MS-PS4-2). |
 How do waves move? How do waves move? (Mastery) |
 What waves do I use? What waves do I use? (Interpersonal) |
 What types of waves are there? What types of waves are there?(Understanding) |
 What can use waves? What can use waves?(Self Expressive) |
|
Bundle 4 B: Waves Practice
Quiz & Espanol Take every day before sleeping! Waves Math Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * > 
|
Vocabulary - Glossary What Are Waves? Chapter 1 Section 1: Pages 13-17: Properties of Waves: Chapter 1, Section 2 Pages 18-23 Chapter 4-1 A Guided Reading Reflection And Mirrors Chapter 4 Section 1: Pages 112-116: Chapter 4-2 A Guided Reading Refraction And Lenses: Chapter 4, Section 2 Pages 117-121 Sound And Light Science Skills Handbookk Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videoss |
Bill Nye: Waves & Espanol Schooltube Video Quiz |
Bill Nye Ligjht Optics & Espanol Schooltube Video Quiz & Esp |

More About Waves Parts Of Waves |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
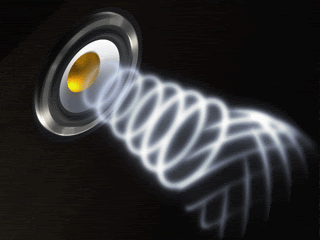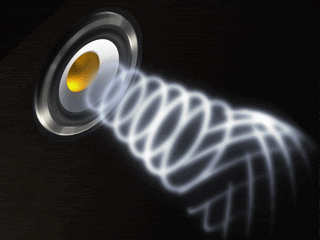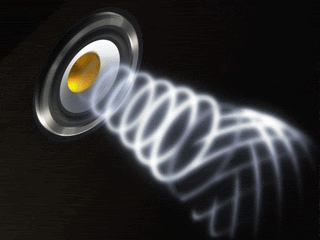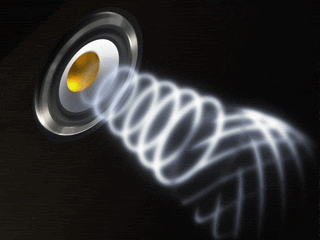
A
wave is a disturbance
that transfers energy from place to place. (i.e. jump rope) Two categories of waves are: a. Mechanical Waves- require a medium to travel through. (i.e. water waves in a pond) b. Electromagnetic Waves- do not need a medium. (i.e. light and radio waves.) A medium is a material through which a mechanical wave travels. |
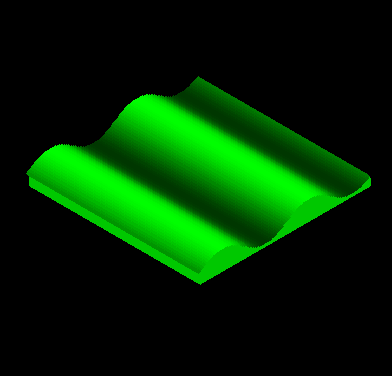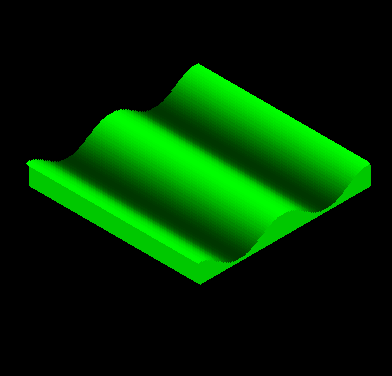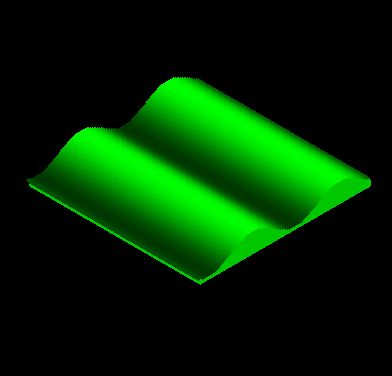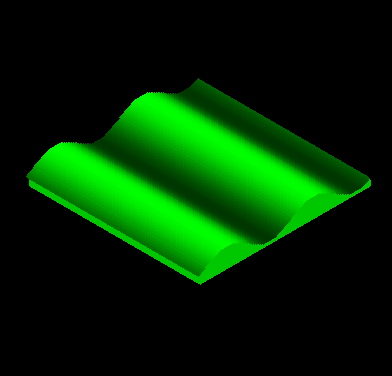 |
Two types of
waves are:  a. Transverse - waves that move the medium at right angles to the direction in which the waves are traveling. The top is a crest and the bottom is a trough. (i.e. like a snake wiggling side to side in an ‘S’ shape) |
 |
b. Longitudinal
- waves move the particles of the medium parallel (the long way) to the
direction that the waves are traveling.  Compression is close together and rarefaction is spread out. (i.e. like a slinky getting squeezed and then opening up) |
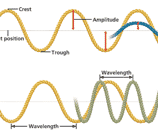 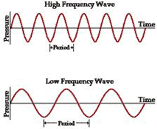 |
Properties
of waves are: a. Amplitude is the maximum distance the particles of a medium move away from their resting point as a wave passes through the medium. b. Wavelength is the distance between two corresponding parts of a wave. c. Frequency is the number of complete waves that pass a given point in a certain amount of time. d. speed is the distance travelled divided by time. speed = wavelength x frequency (= distance / time) |
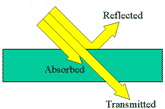 |
When
light strikes an object, the light can be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed. Objects can be transparent, translucent, or opaque. |
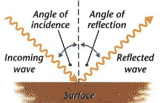 |
When a ray of light hits a surface it bounces
off at an equal and opposite angle. Law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. In regular reflections, parallel rays reflect in parallel, giving a clear image. In diffuse reflections, rays are scattered, |
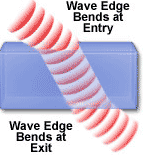 |
Refraction Index of refraction: Light travels at different speeds in different mediums. When a wave enters a medium at an angle, one side of the wave changes speed before the other side, causing the wave to bend or refract. This is how lenses work. |
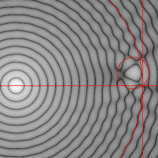 |
Interference
between waves that meet. When two waves pass through each other they can add together to make a larger amplitude or cancel each another out |
 |
Scientist Jean-Baptiste Joseph Fourier (1768-1830) was a French mathematician who worked on how frequencies are related by developing the Fourier Transform/ |
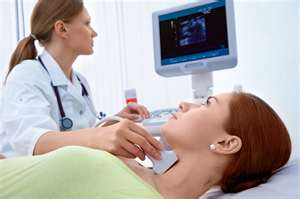 |
Technology Sonograms use sound waves that pass through the medium of the body to make pictures. |