
Unit 4 Assignments

Newton 1-2 Forces
MS-PS2-2

Energy
MS-PS3-1 , MS-PS3-5
Waves
MS-PS4-1, MS-PS4-2
 |
Unit 4 Assignments |
 Newton 1-2 Forces MS-PS2-2 |
 Energy MS-PS3-1 , MS-PS3-5 |
 Waves MS-PS4-1, MS-PS4-2 |
|
Newton's 3rd Law: Collisions |
| Bundle 4 What happens when objects collide? |
| MS-PS2-1
Evidence Statement Apply Newton's Third Law to design a solution to a problem involving the motion of two colliding objects. Packet [Clarification Statement: Examples of practical problems could include the impact of collisions between two cars, between a car and stationary objects, and between a meteor and a space vehicle.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to vertical or horizontal interactions in one dimension.] |
| Motion energy is properly called kinetic energy; it is proportional to the mass of the moving object and grows with the square of its speed (PS3.A as in MS-PS3-1). This idea can be connected to the concept that when the motion energy of an object changes, there is inevitably some other change in energy at the same time (PS3.B as in MS-PS3-5). The concept of motion also connects to the idea that the motion of an object is determined by the sum of the forces acting on it; if the total force on the object is not zero, its motion will change (PS2.A as in MS-PS2-2). The idea of forces connects to the concept that for any pair of interacting objects, the force exerted by the first object on the second object is equal in strength to the force that the second object exerts on the first, but in the opposite direction (PS2.A as in MS-PS2-1). |
Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes |
Vocabulary Action & Reaction: Newton's 3rd Chapter 2 Section 4: Pages 64-69: Rockets & Satellites: Chapter 2 Section 3: Pages 70-72: Reading Essentials Motion Using Force and Motion- National Geographic Defining the Laws of Motion Isaac Newton & the Laws of the Universe Booklet Harcourt-Motion Booklet Motion And Movement Booklet Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
 Action-Reaction Lunar Lander write up an experiment based on this activity. |
Action-Reaction Projectile Motion write up an experiment based on this activity. |
 Collision Lab- Momentum
|
 Momentum Sim write up an experiment based on this activity. |
 Forces and Motion write up an experiment based on this activity. PHet Lab |
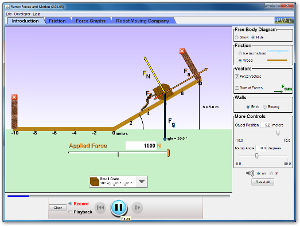 Ramp: Forces & Motion write up an experiment based on this activity. |
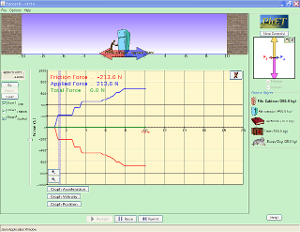 Forces in 1 Dimension write up an experiment based on this activity |
Gizmos- Air Track Lab Crash Momentum Worksheet write up an experiment |
|
Gizmos- Fan Cart Lab Action-Reaction Worksheet write up an experiment |
Gizmos- 2-Dimension Collisions Lab Action-Reaction & Momentum Worksheet write up an experiment |
Gizmos-Sled Wars Graphing Template |
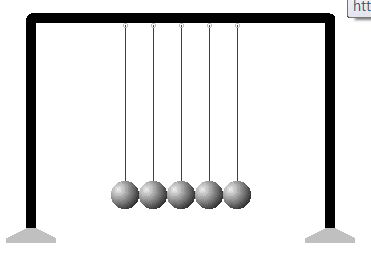 Newton's Cradle write up an experiment based on this activity. |
Cartooning Physics |
 Collisions and Momentum Lab Worksheet |
|
|
| Prentice Hall Video Forces Disney Imagineering: Newton's Laws Viewing Questions |
 Bill Nye |
 |
 |
|
Egg Drop Tech Design
|
 |
 |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
|
Momentum ( M ass * V elocity), Is related to kinetic energy or moving energy. |
 |
The law of conservation of momentum
states that total momentum of any group of objects remains the same
unless an outside force acts on the object.
|
 |
Newton’s third law of motion states that if one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of equal strength in the opposite direction on the first object.
|
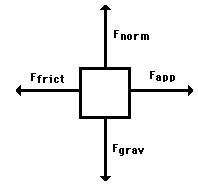 |
Free Body
Diagrams: a standard diagram that shows all of the forces acting
on an object. The object is a box at the center with arrows pointing towards it from the direction of each force. |
 |
Scientists Robert Goddard, the father of rocketry in the early 20th century Wernher von Braun, developed the Atlas rocket for the United States. His rockets were powerful enough for NASA's space program and, along with competing Soviet scientists created intercontinental ballistic missiles that could have destroyed the world. |
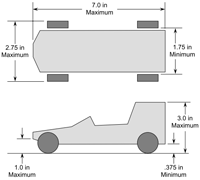 |
Technology Self Propelled Vehicles: use the principles of action-reaction to move themselves by converting stored energy to moving (kinetic) energy Newton Scooters and the Technological Design Cycle |
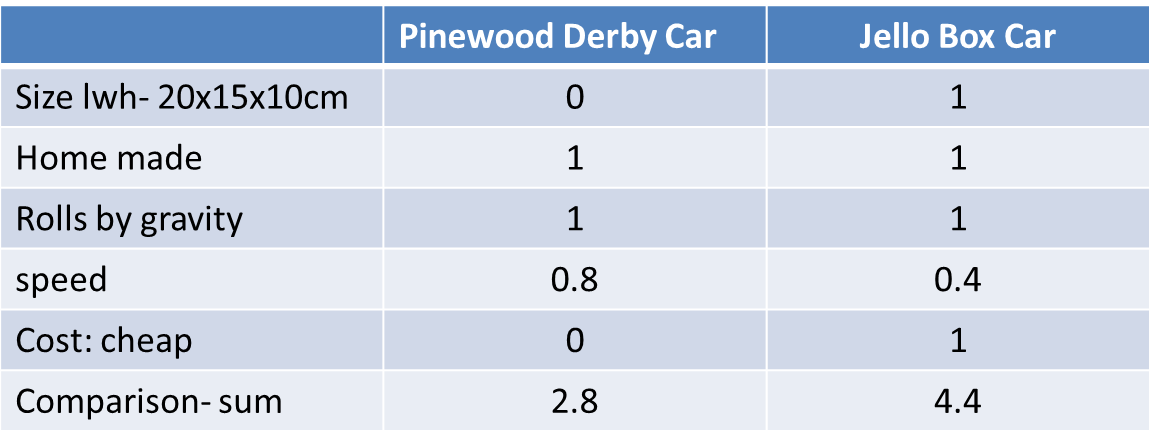 |
Technology Pugh Charts: are used to check if a design meets the specifications (requirements) of a design. Usually used to compare designs (columns) against each specification (rows.)  |