
Unit 4 Assignments
Newton 3 Collisions
MS-PS2-1

Energy
MS-PS3-1 , MS-PS3-5
Waves
MS-PS4-1, MS-PS4-2
 |
Unit 4 Assignments |
Newton 3 Collisions MS-PS2-1 |
 Energy MS-PS3-1 , MS-PS3-5 |
 Waves MS-PS4-1, MS-PS4-2 |
| Newton's
First & Second Laws |
| Bundle 4 What happens when objects collide? |
| MS-PS2-2
Evidence Statement Plan an investigation to provide evidence that the change in an object's motion depends on the sum of the forces on the object and the mass of the object. Packet [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on balanced (Newton's First Law) and unbalanced forces in a system, qualitative comparisons of forces, mass and changes in motion (Newton's Second Law), frame of reference, and specification of units.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to forces and changes in motion in one-dimension in an inertial reference frame and to change in one variable at a time. Assessment does not include the use of trigonometry.] |
| Motion energy is properly called kinetic energy; it is proportional to the mass of the moving object and grows with the square of its speed (PS3.A as in MS-PS3-1). This idea can be connected to the concept that when the motion energy of an object changes, there is inevitably some other change in energy at the same time (PS3.B as in MS-PS3-5). The concept of motion also connects to the idea that the motion of an object is determined by the sum of the forces acting on it; if the total force on the object is not zero, its motion will change (PS2.A as in MS-PS2-2). The idea of forces connects to the concept that for any pair of interacting objects, the force exerted by the first object on the second object is equal in strength to the force that the second object exerts on the first, but in the opposite direction (PS2.A as in MS-PS2-1). |
BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes |
Vocabulary The Nature of Force: Chapter 2 Section 1: Pages 44-51: Force Equation: Newton's 2nd: Chapter 2 Section 2: Pages 52-54: Reading Essentials Motion Using Force and Motion- National Geographic Defining the Laws of Motion Isaac Newton & the Laws of the Universe Booklet Investigating Forces And Motion Harcourt-Motion Booklet MotionAndMovement Booklet Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet (Online Textbook: Log onto Pearson.com, then click on the titles above for the online text.) |
| Labs & Videos |
 Forces and Motion write up an experiment based on this video. PHet Lab |
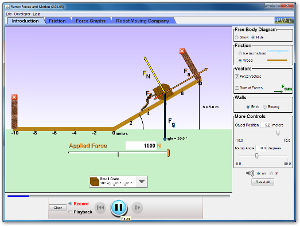 Ramp: Forces & Motion write up an experiment based on this video. |
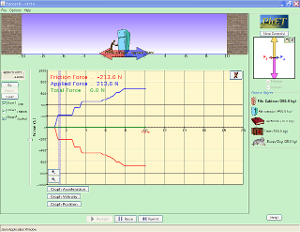 Forces in 1 Dimension write up an experiment based on this video. |
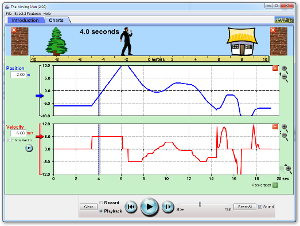 The Moving Man write up an experiment based on this video. |
|
Fan Cart & |
|
|
PS2-2HotWheelsLabWrite-Up Design and run a lab then write up your results- Alternative Minimum Assignment Modified Minimum Assignment |
PS2-2 MarbleLabWrite-Up Design and run a lab then write up your results- Alternative Minimum Assignment Modified Minimum Assignment |
Dr. Zoon Fold-N-RollGravity Cars |
|
| Prentice Hall Video Forces Schlessinger: Forces Disney Imagineering: Newton's Laws Viewing Questions |

Bill Nye Motion Video & Espanol Schooltube Nye Motion Quiz |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live Presentation Project Live Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
A force
is a push or a pull. |
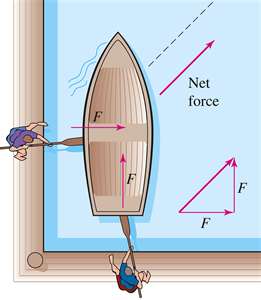 |
Net force
is the sum of forces acting on an object. |
 |
balanced forces: are equal and opposite. They do not cause motion |
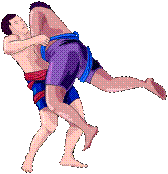 |
unbalanced forces: are not equal. They can cause things to move. |
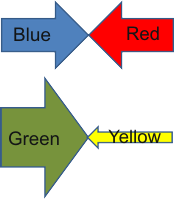 |
Force arrows
show the magnitude and
direction of a force. The width or length can show strength. |
 |
Inertia
is the tendency of an object to resist change to its motion. An
object's inertia is related to its mass. |
 |
Mass is the amount of matter in an object. Matter is anything that has mass and volume (takes up space.) |
 |
Newton’s first
law of motion (aka, The Law of
Inertia) states that "an object at rest remains at rest and an object will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force." |
 |
Newton’s Second
Law of Motion states that the net
force of an object is equal to the net product of it acceleration and
its mass. (i.e. a speeding car has more impact than a blowing leaf crashing into a wall) (Force = Mass * Acceleration) |
 |
Newton’s third law of motion states that if one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of equal strength in the opposite direction on the first object.
|
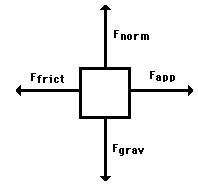 |
Free Body
Diagrams: a standard diagram that shows all of the forces acting
on an object. The object is a box at the center with arrows pointing towards it from the direction of each force. |
|
Momentum ( M ass * V elocity), Is related to kinetic energy or moving energy. |
 |
The law of conservation of momentum
states that total momentum of any group of objects remains the same
unless an outside force acts on the object.
|
 |
Scientist Isaac Newton was a mathematical genius who invented new types of math related to motion and forces. Evidence suggests that he may have had a form of autism. |
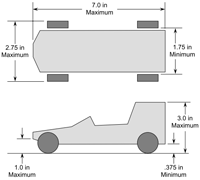 |
Technology Technical Drawings: communicate the measurements of things we build. Gravity Racers and the Technological Design Cycle |
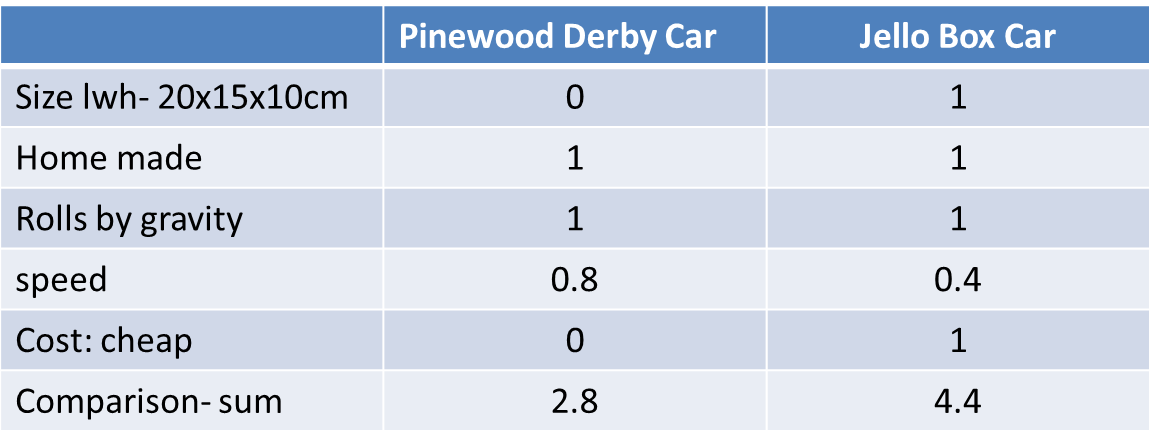 |
Technology Pugh Charts: are used to check if a design meets the specifications (requirements) of a design. Usually used to compare designs (columns) against each specification (rows.)  |