
Unit 4 Assignments
Newton 3 Collisions
MS-PS2-1

Newton 1-2 Forces
MS-PS2-2
Waves
MS-PS4-1, MS-PS4-2

Unit 5 Assignments
Static & Magnets
MS-PS2-5
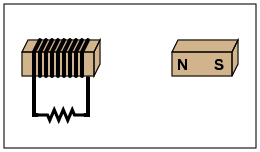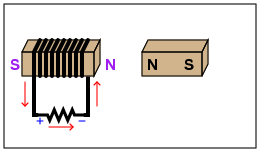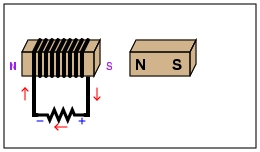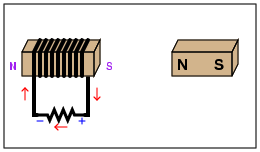
Electromagnets
MS-PS2-3

Gravity
MS-PS2-4
 |
Unit 4 Assignments |
Newton 3 Collisions MS-PS2-1 |
 Newton 1-2 Forces MS-PS2-2 |
 Waves MS-PS4-1, MS-PS4-2 |
 |
Unit 5 Assignments |
 Static & Magnets MS-PS2-5 |
 Electromagnets MS-PS2-3 |
 Gravity MS-PS2-4 |
| Potential & Kinetic Energy |
| Bundle 5 How can objects interact at a distance? |
| MS-PS3-2
Evidence Statement Develop a model to describe that when the arrangement of objects interacting at a distance changes, different amounts of potential energy are stored in the system Packet [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on relative amounts of potential energy, not on calculations of potential energy. Examples of objects within systems interacting at varying distances could include: the Earth and either a roller coaster cart at varying positions on a hill or objects at varying heights on shelves, changing the direction/orientation of a magnet, and a balloon with static electrical charge being brought closer to a classmate’s hair. Examples of models could include representations, diagrams, pictures, and written descriptions of systems.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to two objects and electric, magnetic, and gravitational interactions.] The performance expectation above was developed using the following elements from the NRC document |
| The concept that, when two objects interact, each one exerts a force on the other that can cause energy to be transferred to or from the object (PS3.C as in MS-PS3-2) can connect to the idea that forces that act at a distance (electric and magnetic) can be explained by fields that extend through space (PS2.B as in MS-PS2-5). These ideas also connect to the concept that electric and magnetic (electromagnetic) forces can be attractive or repulsive, and their sizes depend on the magnitudes of the charges, currents, or magnetic strengths involved and on the distances between the interacting objects (PS2.B as in MS-PS2-3). |
| Bundle 4 What happens when objects collide? |
| MS-PS3-1
Evidence Statement Construct and interpret graphical displays of data to describe the relationships of kinetic energy to the mass of an object and to the speed of an object. Packet [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on descriptive relationships between kinetic energy and mass separately from kinetic energy and speed. Examples could include riding a bicycle at different speeds, rolling different sizes of rocks downhill, and getting hit by a wiffle ball versus a tennis ball.] |
| MS-PS3-5
Evidence Statement Construct, use, and present arguments to support the claim that when the kinetic energy of an object changes, energy is transferred to or from the object. Packet [Clarification Statement: Examples of empirical evidence used in arguments could include an inventory or other representation of the energy before and after the transfer in the form of temperature changes or motion of object.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include calculations of energy.] |
| Motion energy is properly called kinetic energy; it is proportional to the mass of the moving object and grows with the square of its speed (PS3.A as in MS-PS3-1). This idea can be connected to the concept that when the motion energy of an object changes, there is inevitably some other change in energy at the same time (PS3.B as in MS-PS3-5). The concept of motion also connects to the idea that the motion of an object is determined by the sum of the forces acting on it; if the total force on the object is not zero, its motion will change (PS2.A as in MS-PS2-2). The idea of forces connects to the concept that for any pair of interacting objects, the force exerted by the first object on the second object is equal in strength to the force that the second object exerts on the first, but in the opposite direction (PS2.A as in MS-PS2-1). |
Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes |
Vocabulary The Nature of Energy Chapter 5 Section 1: Pages 140-147: Energy Conversion and Conservation Chapter 5 Section 2: Pages 148-153: Energy Sources Booklet Energy Booklet Introduction To Energy Booklet Potential & Kinetic Energy Booklet Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet (Online Textbook: Log onto Pearson.com, then click on the titles above for the online text.) |
| Labs & Videos |
|
MS-PS3-2 PhET Skate Park Diagram & Espanol Practice PE 3-2 Potential Energy Storage |
|
VIDEOS
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
Energy Energy is the ability to do work or cause a change. The unit of energy is the Joule. |
 |
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. It depends on mass and velocity. (i.e. a book falling) |
 |
Potential energy is energy that is stored and ready to be released. (i.e. a book on a table ready to fall)
(weight is in newtons, height in meters.) formula for gravity (Earth's = 9.8 m/s2) |
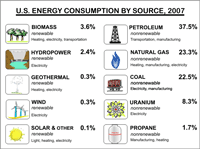 |
Forms of energy and their sources
|
 |
Work is the transfer of energy between objects. (Like a force that makes an object move.) work = force * distance (force is in newtons, distance in meters.) The unit of work is the Joule. |
 |
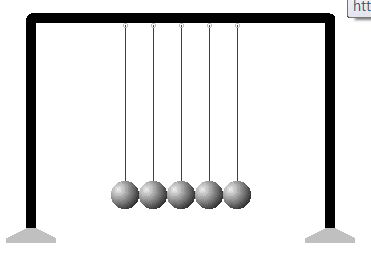
Energy conversion occurs when one type (form) of energy is changed into another. (i.e. electricity into sound, motion into heat, etc.) |
 |
The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Einstein's theory e=mc2 says that energy (e) can be converted to matter (m) and vice versa (and back again). |
 |
Scientist Enrico Fermi, the father of American Nuclear Physics at the University of Chicago. His work is continued in the Manhattan project, Argonne National Labs, and the Fermilab Accelerator in Batavia. |
 |
Technology Lithium Ion Battery Technology: The new hot industry in Michigan is trying to turn cell phone and computer battery technology into a practical electric car. |