
Unit 5 Assignments
Static & Magnets
MS-PS2-5
Electromagnets
MS-PS2-3

Energy
MS-PS3-2
 |
Unit 5 Assignments |
 Static & Magnets MS-PS2-5 |
 Electromagnets MS-PS2-3 |
 Energy MS-PS3-2 |
|
Universal
Gravitation |
| Bundle 5 How can objects interact at a distance? |
|
MS-PS2-4
Evidence Statement Construct and present arguments using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of interacting objects. Packet |
|
BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes |
Vocabulary Universal Gravitation: 2010 Chapter 2 Section 2: Pages 46-47: 1999 Textbook & Audiobook Chapter 2 Section 3 pages 55-61 Gravity & Motion: 2010 Chapter 1 Section 2: Pages 16-19: Reading Essentials Motion Using Force and Motion- National Geographic |
| Labs & Videos |
|
 Gravity Racer design guide |
Gravity Activities
|
Old- Individual Worksheet .ppt
|
|
Disney Imagineering: Gravity Viewing Questions |
Bill Nye |
 |
 |
|
Bill Nye
Friction Video |
 |
 |
 |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
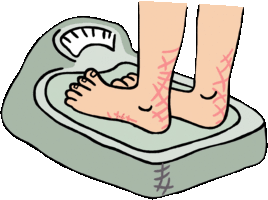 |
Weight
(Mass * Acceleration due to gravity) is the measure of the force of
gravity upon an object. (i.e. you weigh less on the moon, but your mass is the same.) |
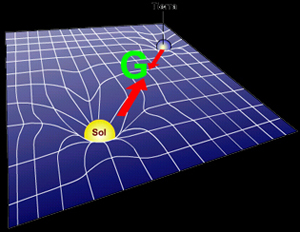 |
The law of universal gravitation states that the
force of gravity acts between all objects (matter) in the universe
(everything, everywhere). |
 |
Gravity
is the force that pulls objects towards more massive things (like Earth). Gravity's strength varies by
|
 |
Newton’s Second
Law of Motion states that the net
force of an object is equal to the net product of it acceleration and
its mass. (i.e. a speeding car has more impact than a blowing leaf crashing into a wall) (Force = Mass * Acceleration) |
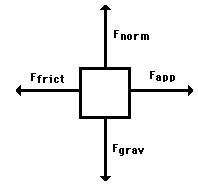 |
Free Body
Diagrams: a standard diagram that shows all of the forces acting
on an object. The object is a box at the center with arrows pointing towards it from the direction of each force. |
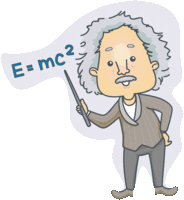 |
Scientist Albert Einstein was a mathematical genius who related time, space, gravity, and mass in his theories of special relativity (Time and space) and general relativity (gravity, space, and mass.) He also defined the speed of light as a universal speed limit and related energy and matter with e=mc2. |
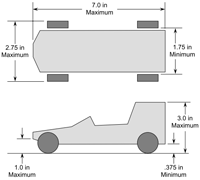 |
Technology Technical Drawings: communicate the measurements of things we build. Gravity Racers and the Technological Design Cycle |
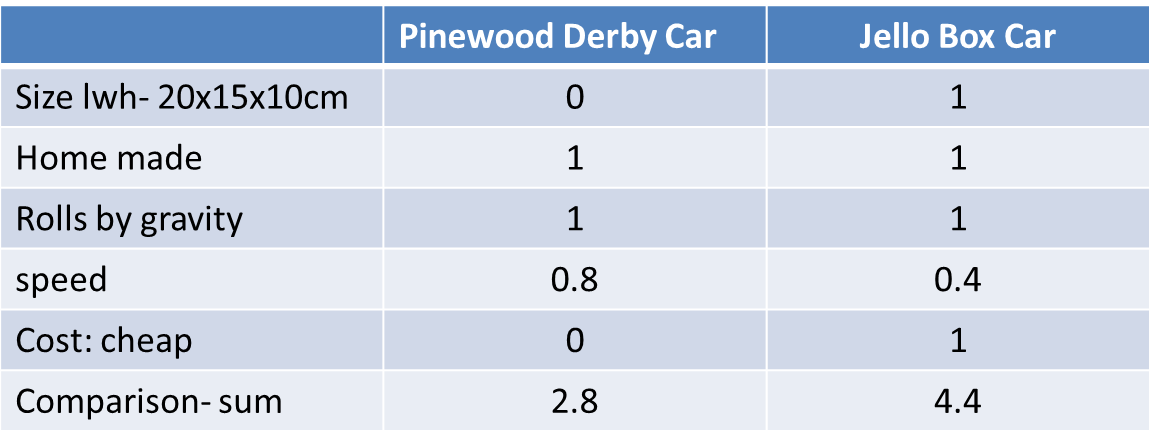 |
Technology Pugh Charts: are used to check if a design meets the specifications (requirements) of a design. Usually used to compare designs (columns) against each specification (rows.)  |