
MS-LS1-3
MS-LS1-8
 |

MS-LS1-3 |

MS-LS1-8 |
| Nervous System |
|
MS-LS1-8
Evidence Statement Gather and synthesize information that sensory receptors respond to stimuli by sending messages to the brain for immediate behavior or storage as memories. Packet |
|
Take every day before sleeping! Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * 
|
Vocabulary - Glossary How The Nervous System Works: Chapter 7 Section 1: Pages 190-195: Divisions Of The Nervous System: Chapter 7 Section 2: Pages 196-205: The Senses: Chapter 7 Section 3: Pages 206-214: Hearing Sound Chapter 2, Section4 Pages 52-61
Human Biology Part 1 Brainworks - Memories and perception games - Reading Guide Understanding Your Brain - Memory and Recall - Reading Guide Head-To-Head - Football Concussions article NG Sound And LightAll About Light and Sound & worksheet Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
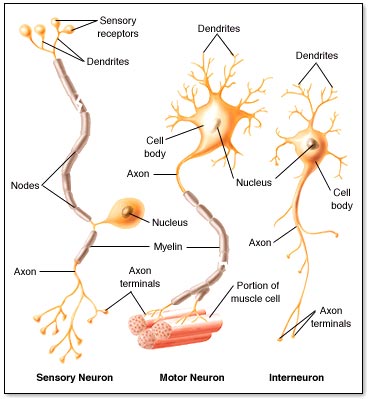 |
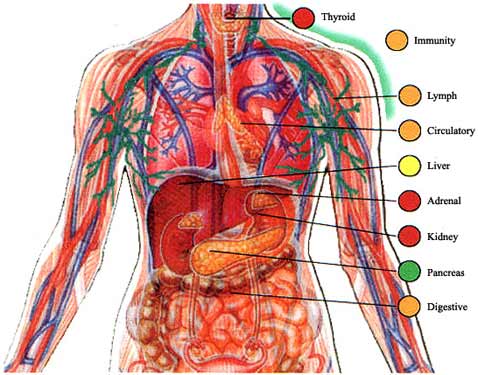
Nerve tissue carries messages back and forth between the brain and every part of your body. Brain, spinal cord, sensory cells in the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and body (touch.) |
 |
Parts of the Nervous System
|
 |
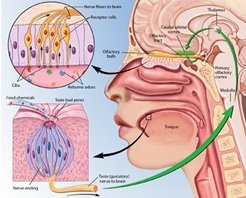
Stimulus and response processing The brain or spinal cord receives information (stimulus) from the sensory organs. Directs response to parts of the body Path of a stimulus
|

|
Memory - Types
|
|
Memory Formation Things that help memory storage, recall and thinking.
|
|
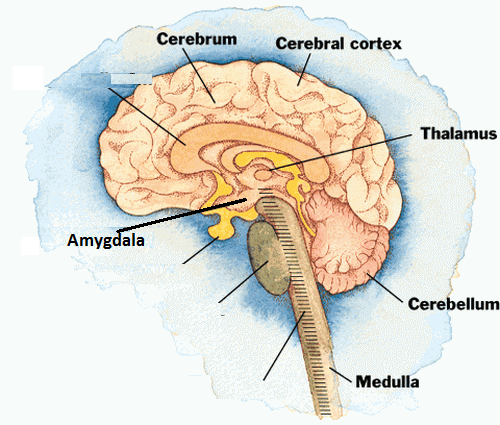
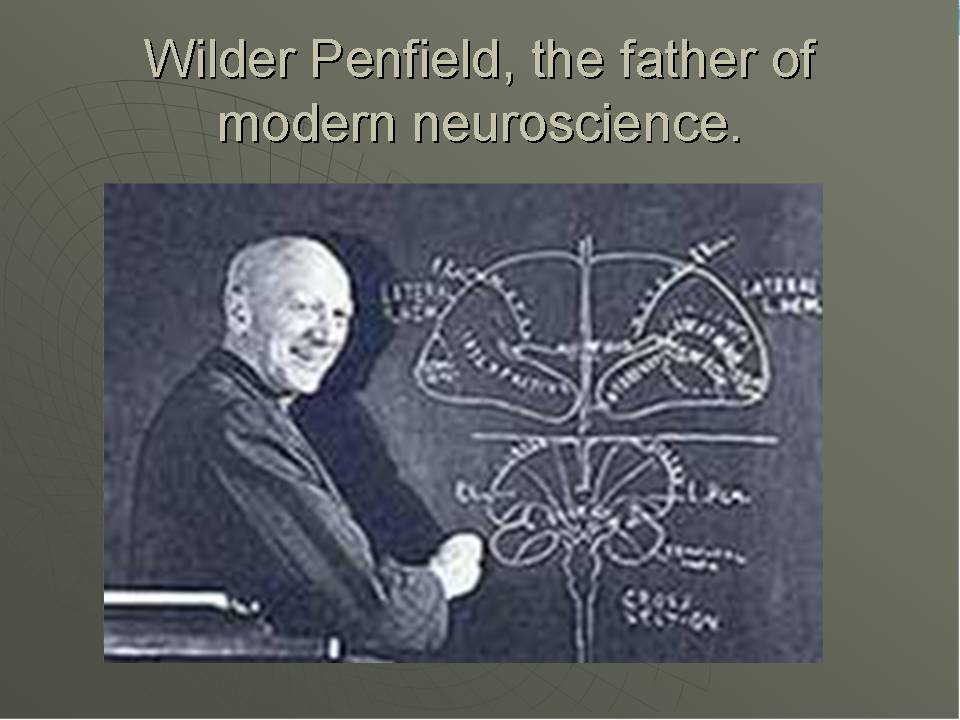
Scientist Wilder Penfield (~1950) Father of Modern Neuroscience- Discovered that low voltage electrodes that touched brains during surgery caused people to remember memories. Each memory had a specific location on the temporal lobe. |
| |
Technology Neural Networks |