
Unit 2 Assignments
Heat
MS-PS1-4, MS-PS3-3, MS-PS3-4
Water Cycle
MS-ESS2-4
Weather & Climate
MS-ESS2-5, MS-ESS2-6
Atoms

Chemistry
 |
Unit 2 Assignments |
Heat MS-PS1-4, MS-PS3-3, MS-PS3-4 |
Water Cycle MS-ESS2-4 |
Weather & Climate MS-ESS2-5, MS-ESS2-6 |
|
Gap Lessons --> |
Atoms |
 Chemistry |
|
Atoms, Structures, & Molecules |
| Bundle 2 How does a change in thermal energy affect matter? |
| MS-PS1-1.
Evidence Statement Develop models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended structures. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on developing models of molecules that vary in complexity. Examples of simple molecules could include ammonia and methanol. Examples of extended structures could include sodium chloride or diamonds. Examples of molecular-level models could include drawings, 3D ball and stick structures, or computer representations showing different molecules with different types of atoms.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include valence electrons and bonding energy, discussing the ionic nature of subunits of complex structures, or a complete description of all individual atoms in a complex molecule or extended structure is not required.] |
| The concept that substances are made from different types of atoms, which combine with one another in various ways (PS1.A as in MS-PS1-1), connects to the ideas that gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other, and in a solid, atoms may vibrate in position but do not change relative locations (PS1.A as in MS-PS1-4) |
|
Take every day before sleeping! Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * 
|
Vocabulary Solids, Liquds, & Gasses: Book K: Chapter 2 Section 1: Pages 44-48: Describing Matter: Book K: Chapter 1 Section 1: Pages 14-21: Matter And Its Changes: Book L: Chapter 1 Section 1: Pages 14-21 Covlent Bonds: Book L: Chapter 2 Section 4: Pages 65-69 Ionic Bonds: Book L: Chapter 2 Section 3: Pages 59-64 Crystal Structures: Book L: Chapter 2 Section5: Pages 72-74 Measuring Matter: Book K: Chapter 1 Section 2 Max Planck Reader Matter Reader Matter Everywhere Booklet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
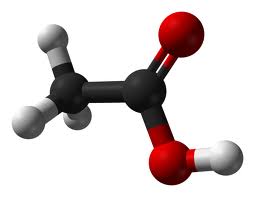 |
A molecule
is a group of atoms that are joined together and act as a single unit. (i.e. a water molecule is made of 2 hydrogen atoms tied to 1 oxygen atom: H2O.) |
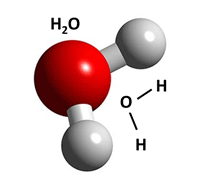 |
A chemical formula (molecular formula) is
the recipe for what is in a molecule. The element symbol Letter goes before the Number of atoms, so H20 has 2 hydrogen & 1oxygen. A structural formula is a way to show how molecules are put together. Lines represent bonds between atoms. |
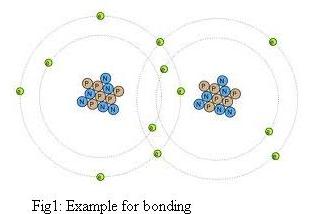 |
Atoms are
held
together in chemical bonds
by sharing, gaining, or losing electrons. A compound is a substance made of two or more elements. |
 |
A mixture is two or
more substances found together. |
| Solution is a very
well-mixed mixture of two substances that keep their properties. (i.e. sugar water vs. salt water) A solvent is a liquid and solute is a solidlike a powder. |
|
 |
Characteristic properties are qualities of a
substance that never change and can be
used to identify the substance. They can be physical properties and chemical properties. |
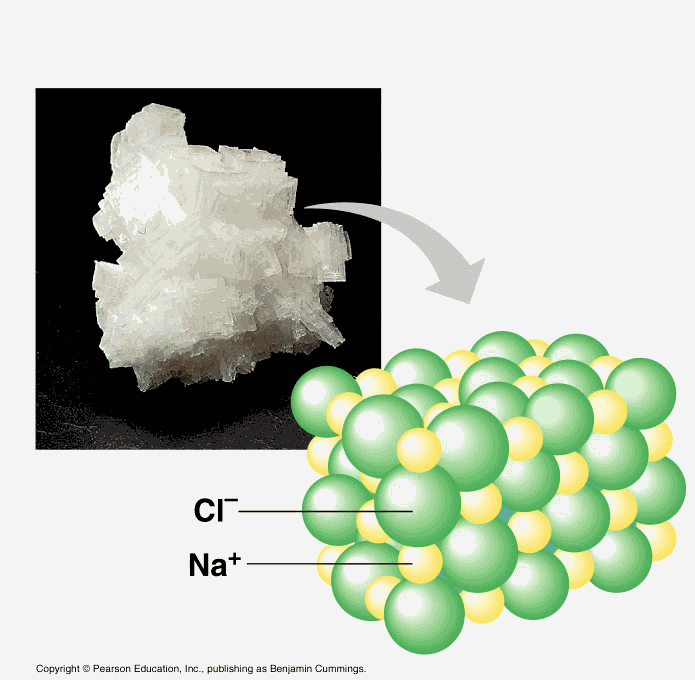 |
Physical properties can be any
property used to characterize
matter and energy and their interactions. They can be observable using instruments or the five senses. (i.e. crystal shape, color, texture, hardness, bends or breaks, density, resistance to water and fire, conductivity or heat or electricity, melting/boiling points) |
 |
Density of a substance is its
mass per unit volume. (mass / volume) |
 |
Physical
changes change the form of a substance, but not its
identity. (i.e. crushing,
folding, freezing, boiling, dissolving, mixing, cutting, twisting ) |
 |
Scientist Craig Venter and Francis Collins decoded the DNA molecule of several life forms, including humans.DNA is one of the largest molecules of all and holds the instructions for how to build the molecules of living things. |
 |
Technology DNA sequencers are machines that can tear apart and read DNA molecules. They were used by Venter & Collins. |