
Heat
B02-Atoms
B03-Matter

Proficiency Standards
 |
Heat |
B02-Atoms |
B03-Matter |
 Proficiency Standards |
| B04
Chemistry |
| How do substances change? |
 How can molecules change? How can molecules change? (Mastery) |
 How can I change molecules? How can I change molecules? (Interpersonal) |
 What types of changes can molecules go through? What types of changes can molecules go through?(Understanding) |
 How are molecules made? How are molecules made?(Self Expressive) |
|
Take every day before sleeping! Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * 
|
Vocabulary Describing Reactions: Chapter 1 Section 2: Pages 24-31: Controlling Reactions: Chapter 1 Section 3: Pages 32-37: Acids & Bases Antoine Lavoisier Reader Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
Chemical properties are how a
substance reacts and changes with other substances under which
conditions. |
 |
In chemical changes
/ reactions one or more substances combine or break
apart to form new substances. (i.e. burned wood becomes charcoal, water vapor, and carbon dioxide gas) |
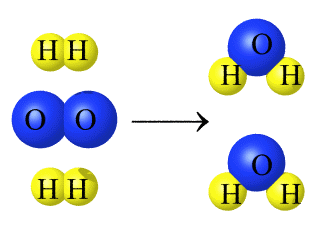 |
Chemical equations show the
reactants and products of a reaction on either side
of an arrow showing the direction of the reaction. |
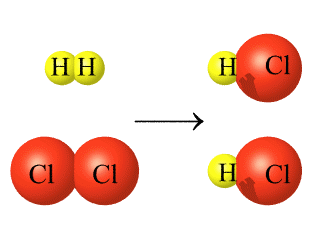 |
conservation
of mass: matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical
reaction. A balanced chemical equation shows this by having the same number of atoms on both sides of the equation. |
 |
Bonds store energy that is related to thermal energy.
|
 |
Reaction
rates are the speed that a substance enters into a chemical reaction.
Reactions can be controlled using 1. concentration: how much chemical is present (the flask limits oxygen) 2. surface area: how much is exposed to the reaction (powder versus block) 3. temperature: thermal energy often speeds reactions 4. catalysts/enzymes: molecules that help the reaction 5. inhibitors: molecules that slow reactions |
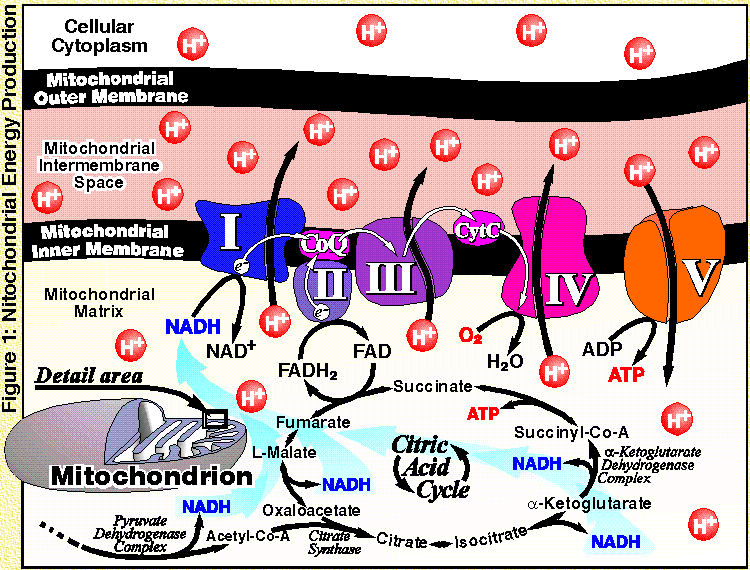 |
Scientist Hans Adolf Krebs- Nobel Prize winner- discovered how energy molecules are made in living cells in the citric acid or Krebs cycle. |
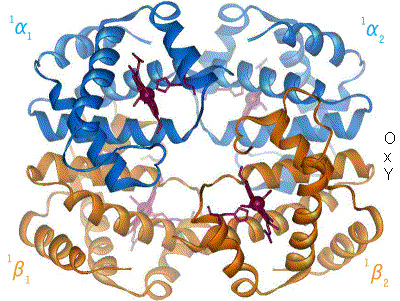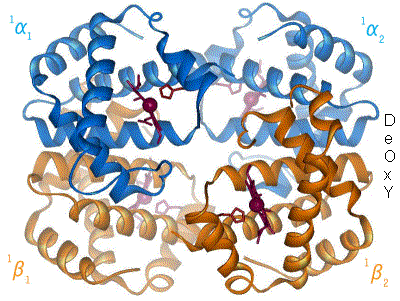 |
Technology Proteomics is the study of how the molecular machines called proteins that run almost everything in our bodies work. We can now use DNA gene technology to make or fix proteins. The protein hemoglobin in our red blood cells carries oxygen. |