
Unit 2 Assignments

Matter
MS-PS1-1
Water Cycle
MS-ESS2-4
Weather & Climate
MS-ESS2-5, MS-ESS2-6
Atoms & Elements

Pressure
 |
Unit 2 Assignments |
 Matter MS-PS1-1 |
Water Cycle MS-ESS2-4 |
Weather & Climate MS-ESS2-5, MS-ESS2-6 |
|
Gap Lessons --> |
 Atoms & Elements |
 Pressure |
| Heat |
| Bundle 2 How does a change in thermal energy affect matter? |
| MS-PS1-4.
Evidence Statement Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on qualitative molecular-level models of solids, liquids, and gases to show that adding or removing thermal energy increases or decreases kinetic energy of the particles until a change of state occurs. Examples of models could include drawing and diagrams. Examples of particles could include molecules or inert atoms. Examples of pure substances could include water, carbon dioxide, and helium.] |
| MS-PS3-3
Evidence Statement Apply scientific principles to design, construct, and test a device that either minimizes or maximizes thermal energy transfer.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of devices could include an insulated box, a solar cooker, and a Styrofoam cup.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include calculating the total amount of thermal energy transferred.] |
| MS-PS3-4
Evidence Statement Plan an investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred, the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic energy of the particles as measured by the temperature of the sample. [Clarification Statement: Examples of experiments could include comparing final water temperatures after different masses of ice melted in the same volume of water with the same initial temperature, the temperature change of samples of different materials with the same mass as they cool or heat in the environment, or the same material with different masses when a specific amount of energy is added.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include calculating the total amount of thermal energy transferred.] |
| In science, heat refers to the energy transferred due to the temperature difference between two objects (PS3.A as in MS-PS1-4); this connects to the idea that temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles of matter (PS3.A as in MS-PS3-3). These ideas also connect to the concept that the amount of energy transfer needed to change the temperature of a matter sample by a given amount depends on the nature of the matter, the size of the sample, and the environment (PS3.A as in MS-PS3-4). |
|
Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes |
Vocabulary Temperature and Thermal Energy and Audiobook Chapter 6 Section 1: Pages 167-170: The Nature of Heat and Audiobook Chapter 6 Section 2: Pages 171-177 Thermal Energy and States of Matter Chapter 6 Section 3: Pages 181-186 Uses of Heat Chapter 6 Section 4: Pages 187-190 Heat Booklet Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Pearson Videos States of Matter |
Pearson Videos |
Pearson Videos Thermal Energy and Heat |
Liquid Convection Mpeg4 |
Bill Nye Phases of Matter Video Quiz Bill Nye Heat Video Schooltube Espanol Quiz |
|
 |
 Heat |
 |
 Cooking With Heat Transfer Conduction Race |
 Heat Transfer |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| ReReading & Math Work |
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
 |
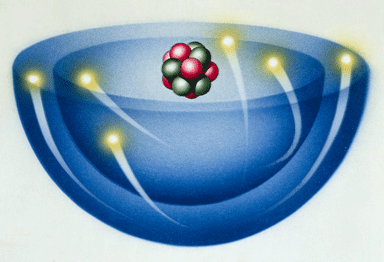
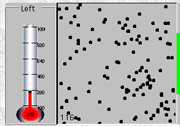
Temperature
is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the individual particles (i.e. two units of temperature are degrees Fahrenheit (�F) and degrees Celsius (�C). absolute zero is the lowest temperature possible. atoms stop moving. |
 |
Thermal
energy is the total energy of all of the particles in a system. |
 |
Heat is thermal energy moving
from warmer objects to cooler objects. |
 |
Heat
is transferred (moved) in three ways: a. Conduction - the process of heat being transferred from one particle of matter to another without the movement of matter itself. (i.e. by touch) |
 |
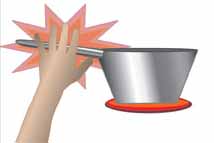
b.
Convection - the
movement that transfers heat by
the movement of currents within a fluid. (i.e. a fire’s heat rises & warms the air above, cool air falls) |
 |
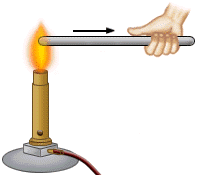
c.
Radiation
- the transfer of energy by the
electromagnetic waves. (i.e. heat from a fire warms your hands and face from a distance) |
 |
Conductors
are materials that conduct
energy well. (i.e. metal pot handles, copper wire) |
 |
Insulators are materials
that do not conduct energy
well. (i.e. pot holders, plastic coating on wires) |
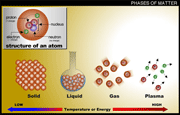 |
The states of matter are:
|
 |
The specific
heat of a substance is the amount of energy required to raise the
temperature of 1 kilogram by 1 degree celsius (or kelvin) |
| Scientist |
|
 |
Technology Electric heaters convert electrical energy into heat. The heat moves by radiation. Fans can move it by convection. |