
Unit 2 Assignments

Matter
MS-PS1-1
Heat
MS-PS1-4, MS-PS3-3, MS-PS3-4
Weather & Climate
MS-ESS2-5, MS-ESS2-6
 |
Unit 2 Assignments |
 Matter MS-PS1-1 |
Heat MS-PS1-4, MS-PS3-3, MS-PS3-4 |
Weather & Climate MS-ESS2-5, MS-ESS2-6 |
| Water Cycle |
| Bundle 2 How does a change in thermal energy affect matter? |
| MS-ESS2-4
Evidence Statement Develop a model to describe the cycling of water through Earth's systems driven by energy from the sun and the force of gravity. Packet [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the ways water changes its state as it moves through the multiple pathways of the hydrologic cycle. Examples of models can be conceptual or physical.] [Assessment Boundary: A quantitative understanding of the latent heats of vaporization and fusion is not assessed.] |
| These concepts of energy transfer connect to the idea that the ocean exerts a major influence on weather and climate by absorbing energy from the sun, releasing it over time, and globally redistributing it through ocean currents (ESS2.D as in MS-ESS2-6), which in turn connects to the idea that global movements of water and its changes in form are propelled by sunlight and gravity (ESS2.C as in MS-ESS2-4). These concepts also connect to the idea that complex patterns of the changes and the movement of water in the atmosphere, determined by winds, landforms, and ocean temperatures and currents, are major determinants of local weather patterns (ESS2.C as in MS-ESS2-5). |
Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * 
|
Vocabulary - Glossary Water Cycle Chapter 1 Section 3: Pages 32-37: Guided Reading Properties of Water: Chapter 1, Section 2 Pages 23-31 : Water On Earth Excerpts Chapter 1, Section1 Pages 20-24 River Structure Diagram Pages 48-49 Booklets
Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
 Glaciers PHET write up an experiment based on this activity. |
Phases of Water Gizmo Gizmos Lab packet doc & |
 Greenhouse Effect PHET write up an experiment based on this activity. |
 ETE Water Cycle informational page |
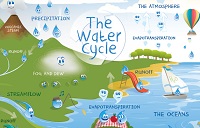 USGS Kids' Water Cycle |
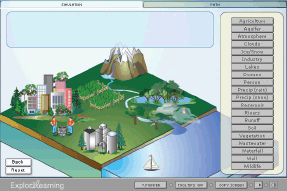 Gizmos Water Cycle Worksheet PE Practice |
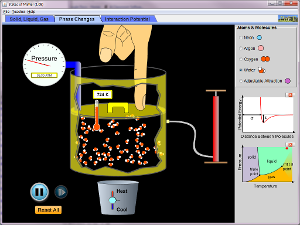 States Of Matter Worksheet based on this activity. |
|
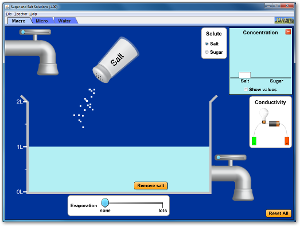 Sugar and Salt Solutions conductivity, concentration, evaporative and crystal formation |
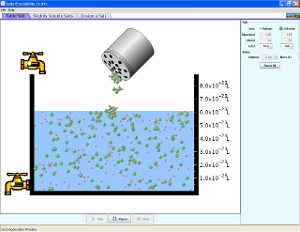 Salts & Solubility Solutions |
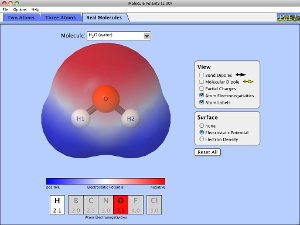 Molecules & Charge write up an experiment based on this activity. |
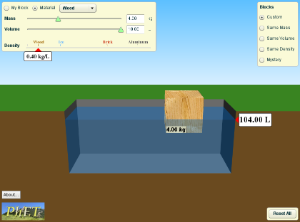 Density write up an experiment based on this activity. |
|
NGSS - ESS 2-4 Earth's Systems Develop a model to describe the cycling of water through Earth's systems driven by energy from the sun and the force of gravity. |
PH Science Explorer Earth- The Water Planet |
 Visual Periodic Table |
|
| Bill Nye: Water Cycle Espanol & Quiz Rivers & Streams & Quiz Oceanography & Quiz |
PBS Life of a Glacier informational page Science Flix Tornado in a bottle |
  |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
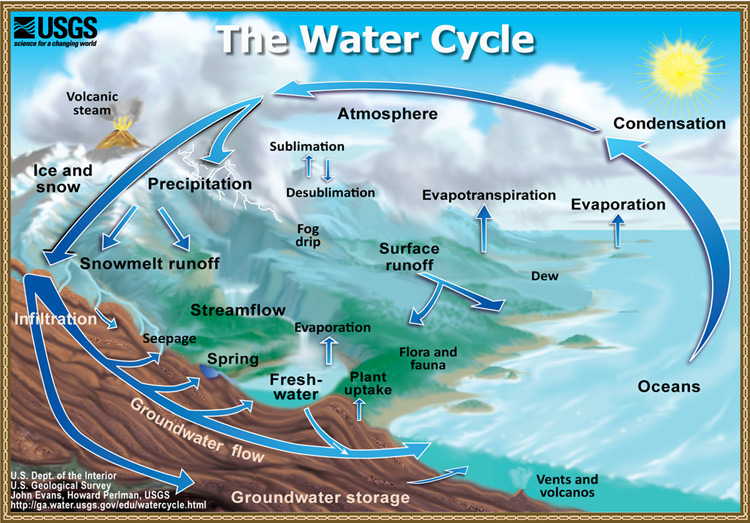 |
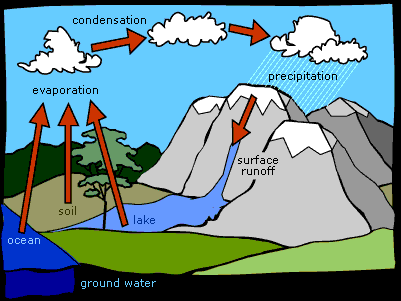
The
water cycle
aka hydrologic cycle
is the continuous process by which water moves through the living and
nonliving parts of the environment. In the water cycle, water moves from bodies of water, land, and living things on Earth's surface to the atmosphere aand back to Earth's surface. |
 |
Properties of Water
|
 |
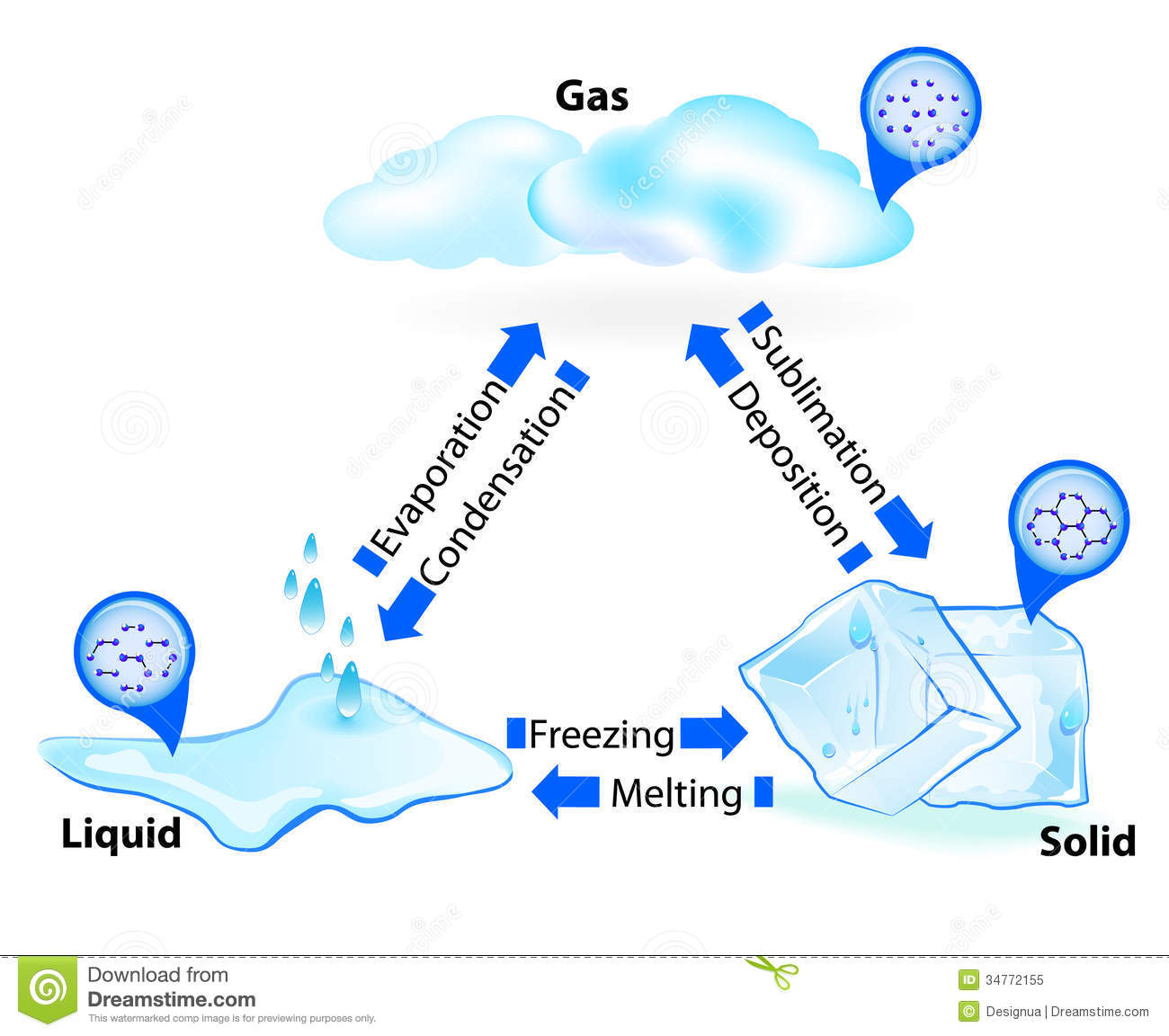
Evaporation – liquid water becomes water vapor, a gas, in the atmosphere when water molecules at the surface of oceans, lakes, soil, puddles and our skin have absorbed enough heat (thermal) energy from the sun to change state. (textbook p.32/33) |
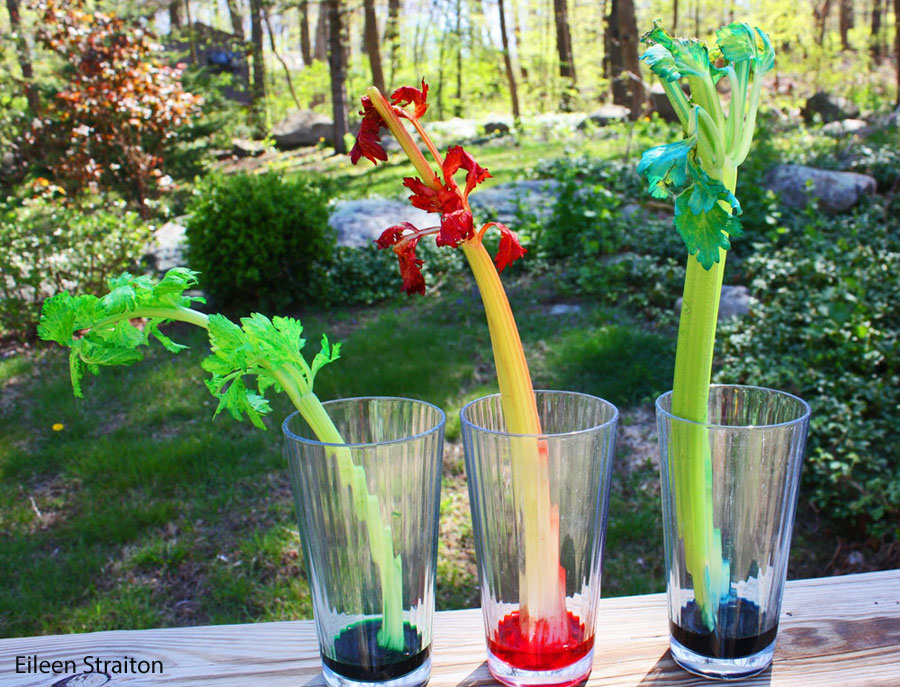 |
Plant uptake – plants draw in water from the soil through their roots. (textbook p.33) |
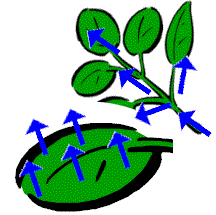 |
Transpiration – plants give off water through the leaves (occurs on the underside of leaves, through openings called stomata) in the form of water vapor. (textbook p.33/34) |
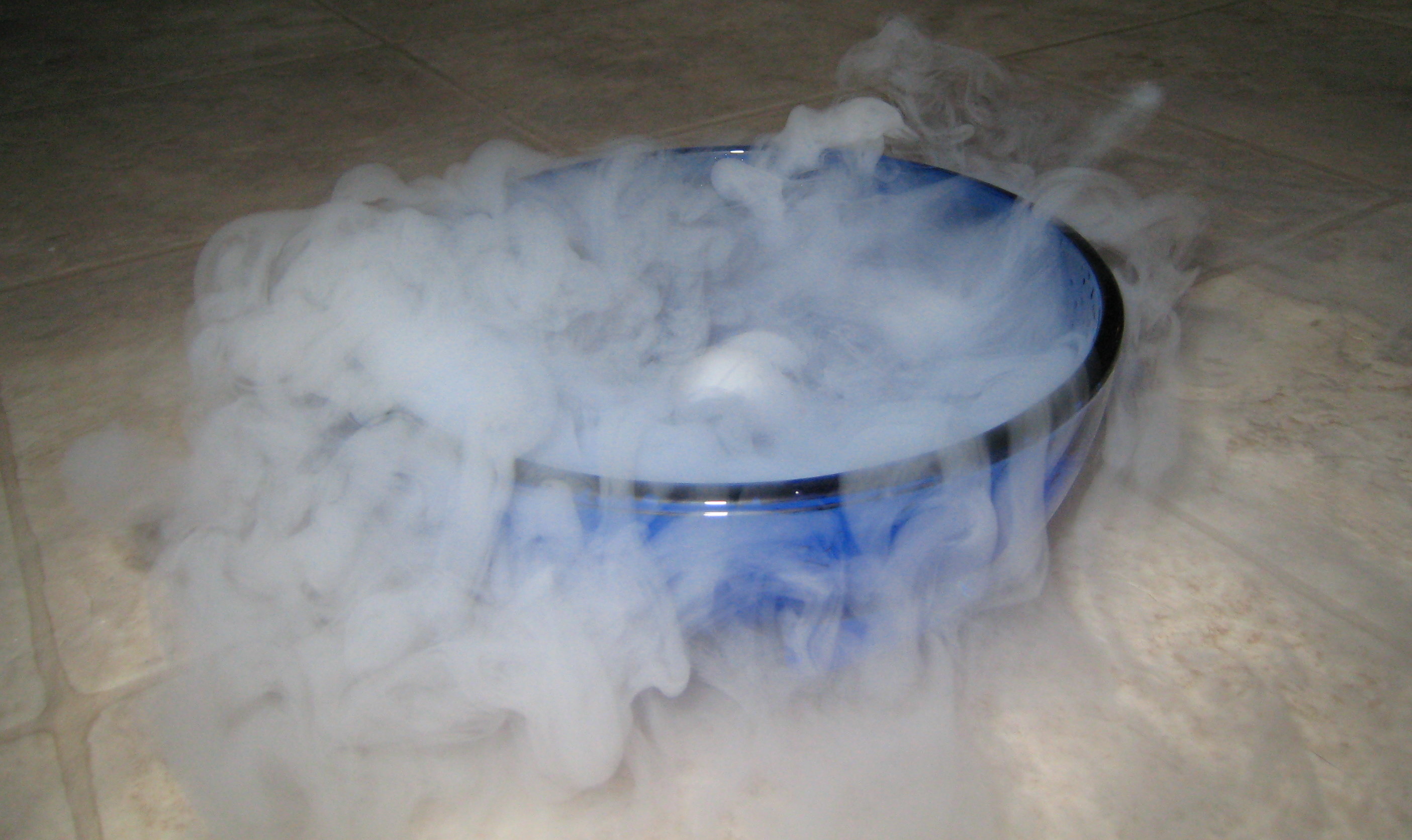 |
Sublimation – tiny amounts of water vapor enter the air from ice (glaciers and icebergs), when water passes directly from the solid state to the gaseous state. (textbook p.34) |
 |
Condensation – gaseous water vapor in the atmosphere changes into liquid water or solid ice crystals (deposition – phase change from gas straight to solid, forming the ice crystals that we know as snow), in the form of a cloud, when water vapor condenses as it cools and releases thermal energy. (textbook p.34) |
 |
Precipitation – water that falls to Earth due to gravity as rain, snow, sleet or hail when the water (solid or liquid) becomes too heavy for the cloud. (textbook p.34) |
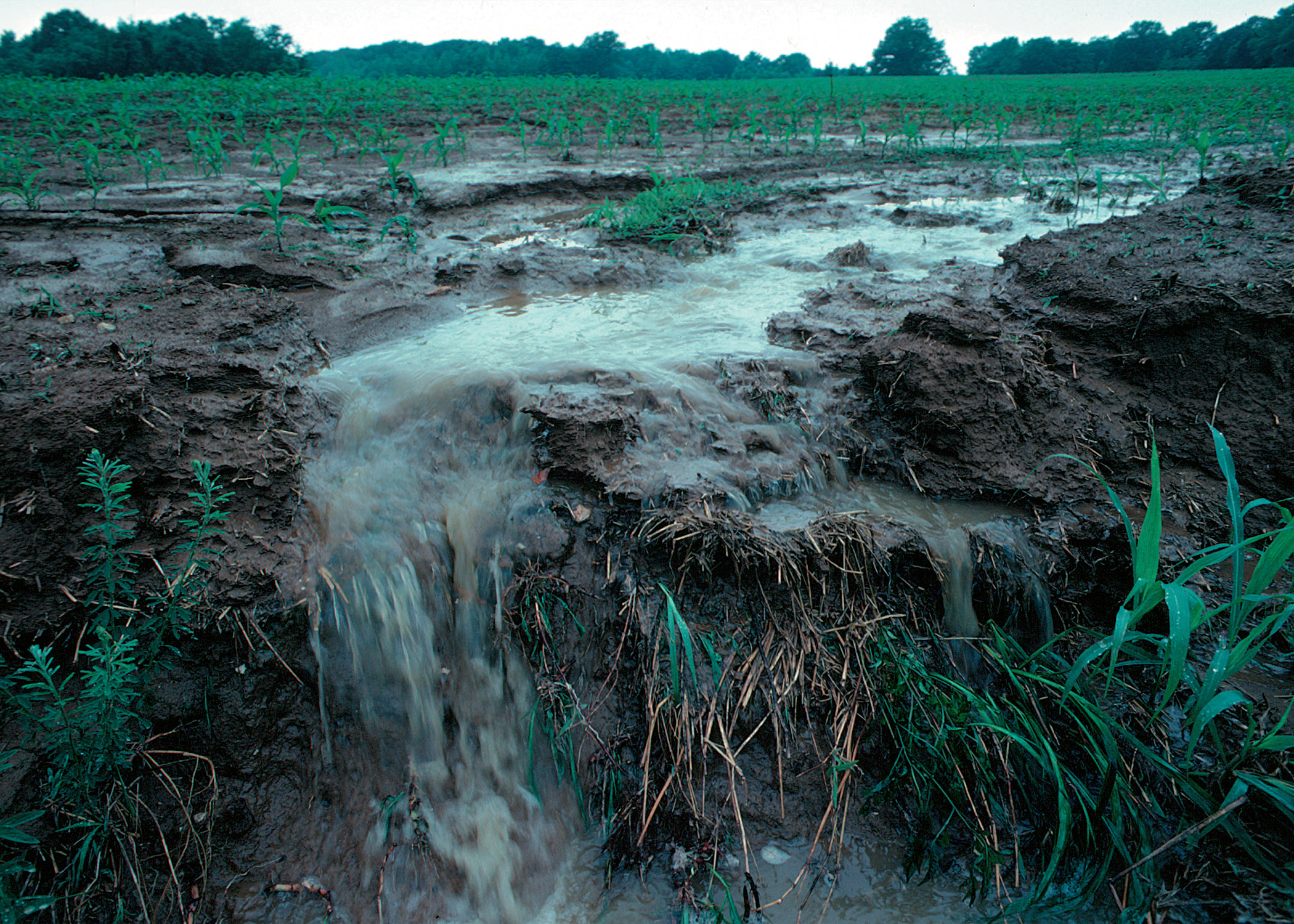 |
Runoff – when precipitation falls on land, some of the
water runs off the surface of the land into rivers, lakes and oceans.
(textbook p.34/35)
|
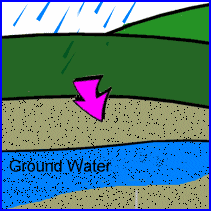 |
Infiltration – water trickles down into the ground and
forms groundwater. Groundwater may move underground until it reaches a
river, lake or ocean. (textbook p.35)
|
 |
Animal consumption – some water passes through living
things. Animals and people drink water and eventually release it back to
the environment as waste. (textbook p.35)
|
| |
|
| Scientist |
|
| |
Technology |