
Unit 3 Assignments
Cell Theory
MS-LS1-1
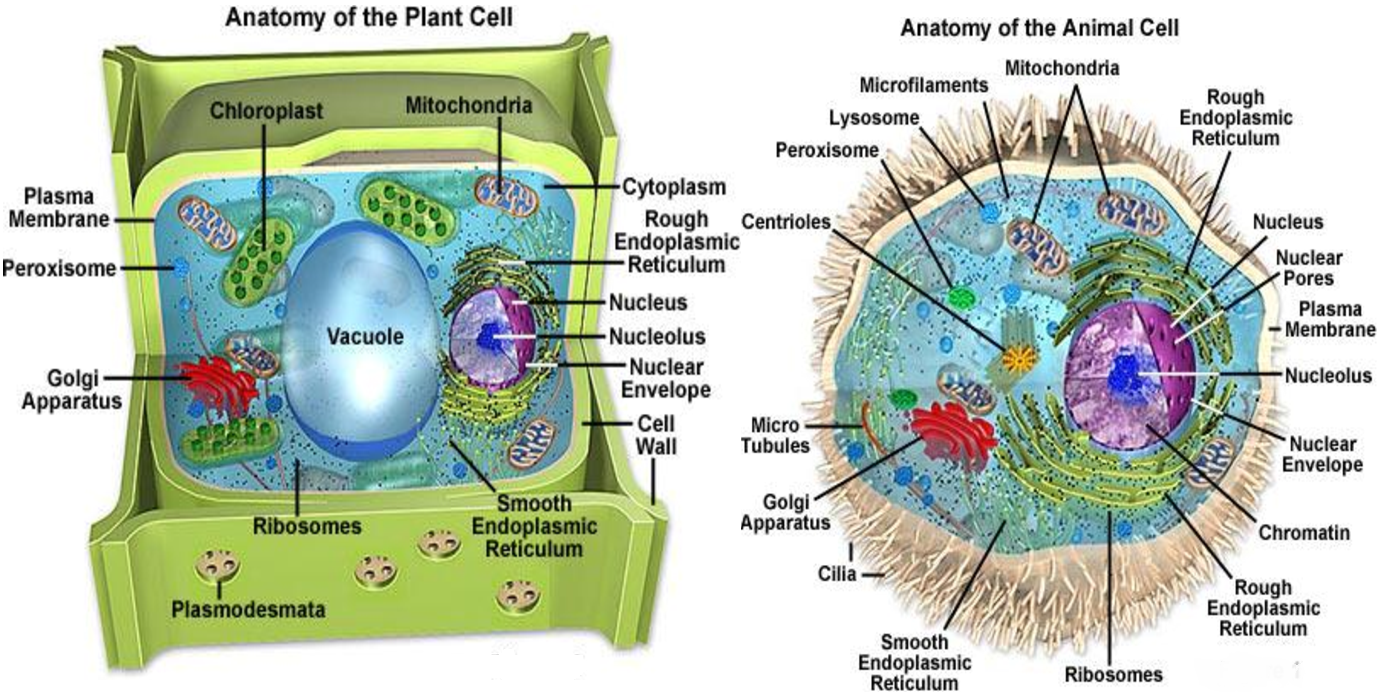
Cell Structures
MS-LS1-2
 |
Unit 3 Assignments |
 Cell Theory MS-LS1-1 |
 Cell Structures MS-LS1-2 |
| Human Body Systems |
| Bundle 3 Why are bones so hard? |
|
MS-LS1-3
Evidence Statement Use argument supported by evidence for how the body is a system of interacting subsystems composed of groups of cells. Packet |
| In multicellular organisms, the body is a system of multiple interacting subsystems, which are groups of cells that work together to form tissues and organs that are specialized for particular body functions (LS1.A as in MSLS1-3). |
| All living things are made up of cells, which is the smallest unit that can be said to be alive. An organism may consist of one single cell (unicellular) or many different numbers and types of cells (multicellular) (LS1.A as in MS-LS1-1). Within cells, special structures are responsible for particular functions, and the cell membrane forms the boundary that controls what enters and leaves the cell (LS1.A as in MS-LS1-2). In multicellular organisms, the body is a system of multiple interacting subsystems, which are groups of cells that work together to form tissues and organs that are specialized for particular body functions (LS1.A as in MSLS1-3). |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |
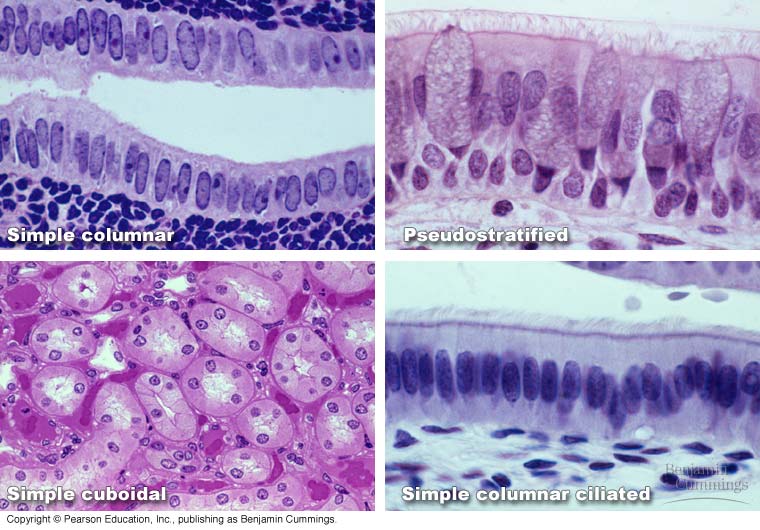 |
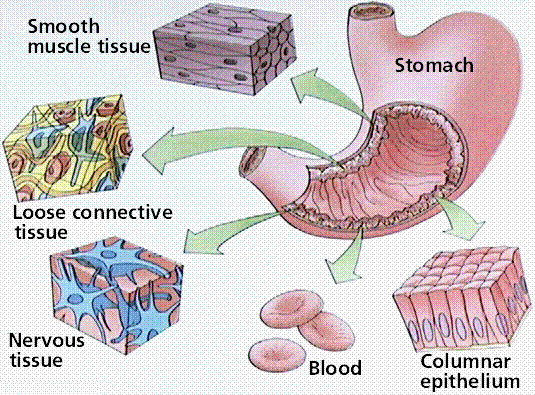
Tissue - systems of cells working
together for a specific purpose. All cells come from a single type of stem cell that can differentiate to become all other cells in your body. Thereare four types of cells in humans epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve. |
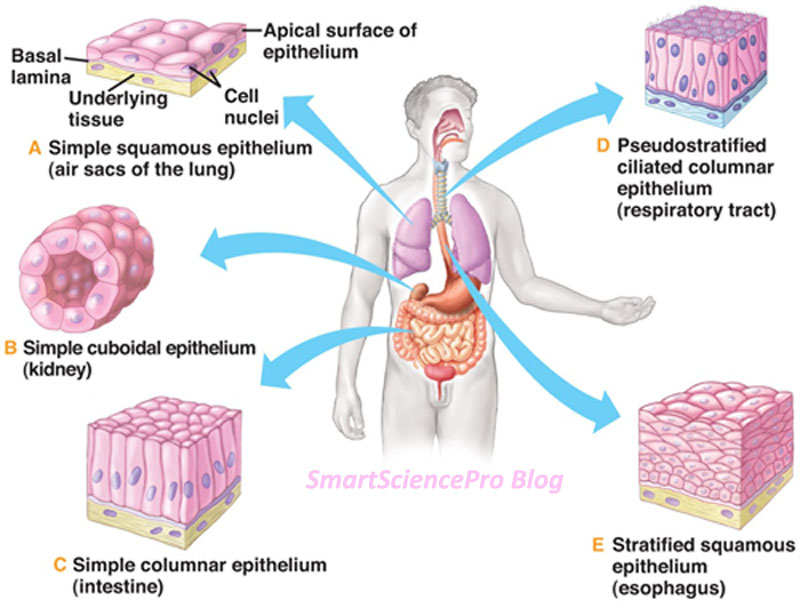
|
Epithelial Tissue covers the inside and outside surfaces of the body, protecting it. Skin, organ lining, digestive tract lining. |
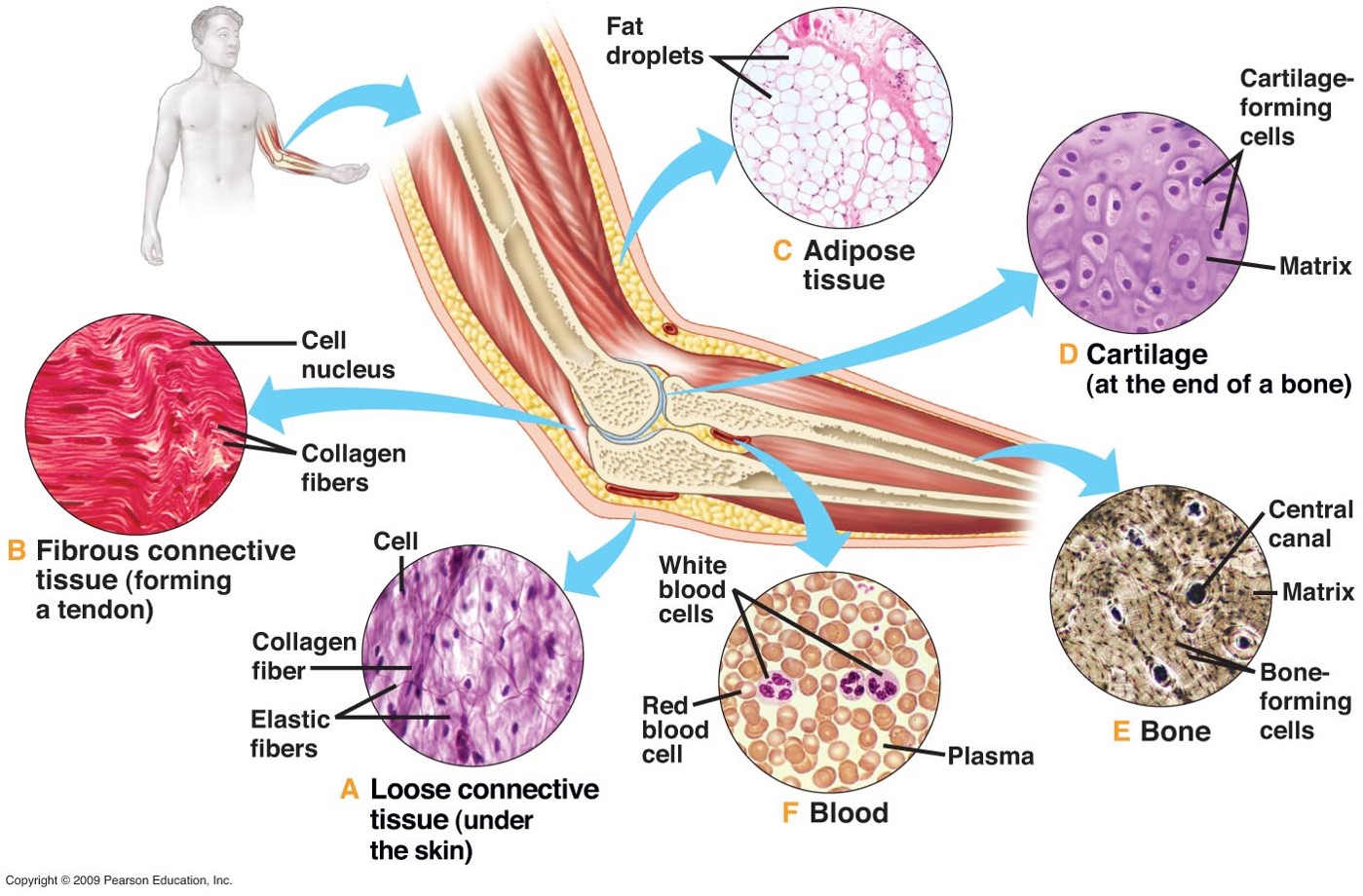 |
Connective Tissue supports the body and connects its parts. Bones, fat, cartilage, tendons, blood, etc. |
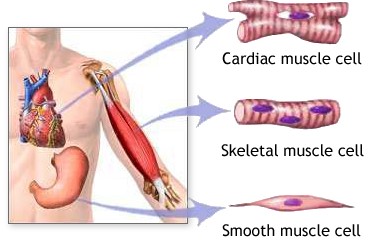 |
Muscle tissue can contract or shorten (it does not lengthen.) It makes all movements of the body. Heart, digestive muscles, etc. |
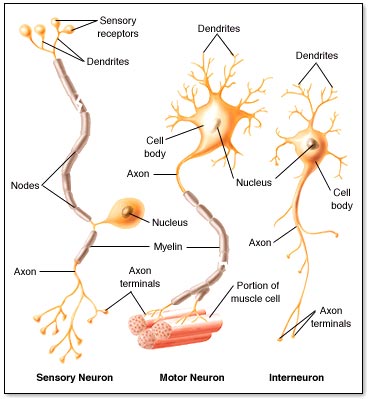 |
Nerve tissue carries messages back and forth between the brain and every part of your body. Brain, spinal cord, sensory cells in the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and body (touch.) |
 |
An organ is a structure made of different kinds of tissue.
Heart, lungs, kidney, etc An organ system is a group of organs that work together. For example, the nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, eyes, ears, tongue, nose, sensory nerves, etc. |
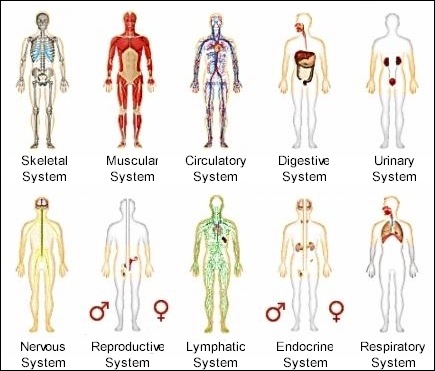 |
Systems of the humand body
|
|
Scientist Wilder Penfield (~1950) Father of Modern Neuroscience- Discovered that low voltage electrodes that touched brains during surgery caused people to remember memories. Each memory had a specific location on the temporal lobe. |
| |
Technology Neural Networks |