
Unit 3 Assignments
Cell Theory
MS-LS1-1
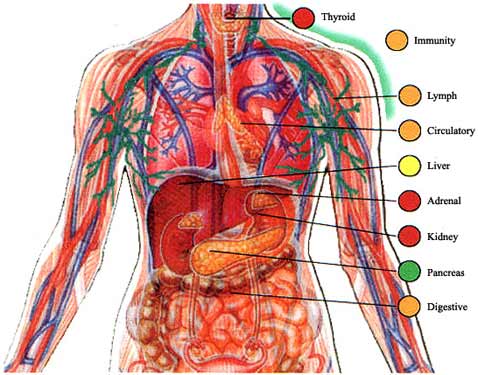
Human Body
MS-LS1-3
 |
Unit 3 Assignments |
 Cell Theory MS-LS1-1 |
 Human Body MS-LS1-3 |
| Cell Structures |
| Bundle 3 Why are bones so hard? |
|
MS-LS1-2
Evidence Statement Develop and use a model to describe the function of a cell as a whole and ways parts of cells contribute to the function. Packet |
| Within cells, special structures are responsible for particular functions, and the cell membrane forms the boundary that controls what enters and leaves the cell (LS1.A as in MS-LS1-2). In multicellular organisms, the body is a system of multiple interacting subsystems, which are groups of cells that work together to form tissues and organs that are specialized for particular body functions (LS1.A as in MSLS1-3). |
| All living things are made up of cells, which is the smallest unit that can be said to be alive. An organism may consist of one single cell (unicellular) or many different numbers and types of cells (multicellular) (LS1.A as in MS-LS1-1). Within cells, special structures are responsible for particular functions, and the cell membrane forms the boundary that controls what enters and leaves the cell (LS1.A as in MS-LS1-2). In multicellular organisms, the body is a system of multiple interacting subsystems, which are groups of cells that work together to form tissues and organs that are specialized for particular body functions (LS1.A as in MSLS1-3). |
|
Practice Quiz: Cell Structures & Espanol (graded) Take every day before sleeping! Vocabulary Review Activities BrainPop Animations and Practice Quizes * 
|
Vocabulary - Glossary Loooking Inside Cells: Chapter 1 Sections 2 Pages 23-31: Reading Essentials Booklets
Science Skills Handbook Appendix: Pages 202-214: Process Skills Packet |
| Labs & Videos |
| Engage Discrepant Event |
Explore Research |
Explain Write-Up |
Elaborate New situations/applications |
Evaluate project to share |
| Reading & Math Work |
|
|
| Projects by Learning Style and Media Type |
 Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery) Sensing-Thinking
(Mastery)Facts
|
 Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal) Sensing-Feeling
(Interpersonal)A time when you...
|
 Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding) Intuitive-Thinking
(Understanding)Playing with facts
|
 Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive) Intuitive-Feeling
(Self-Expressive)Creating new possibiliteis
|
|
|
|
 Live
Presentation Project Live
Presentation Project
|
| Essential Vocabulary & Concepts |
| Picture | Core Knowledge or
Concept |

|
Characteristics of Living Organisms
(Life Processes):
|

|
Robert Hooke first saw cork cells (left) through a
microscope and descirbed them in his book Micrographia in 1665. Cell Theory:
|
|
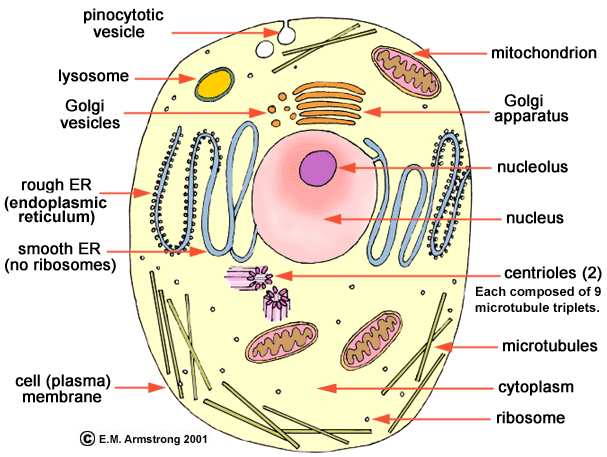
Animal Cells have cell membranes and burn sugars from
food they consume through cellular respiration to produce energy. Parts of animal cells
|
|
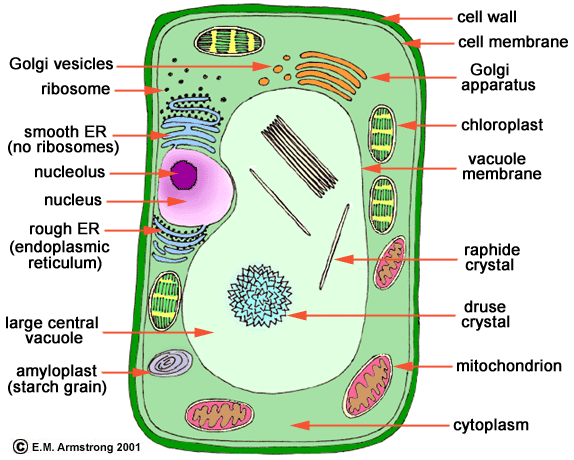
Plant cells have a rigid cell wall and produce sugars in their
chloroplasts through photosynthesis. Parts of Plant Cells
|
Protista (eukaryotes) are unicellular (single-celled) organisms.
|
|
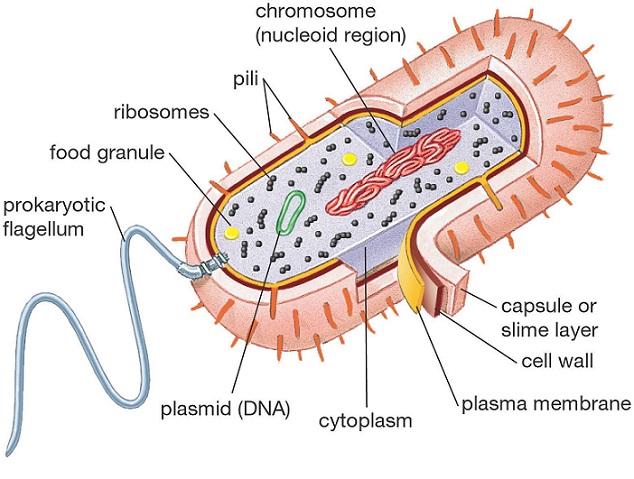 |
Bacteria (prokaryotes) are usually simpler single-celled organisms with cell walls and a nucleoid with DNA rings called plasmids. They are usually much smaller than protists and both animal and plant cells. |
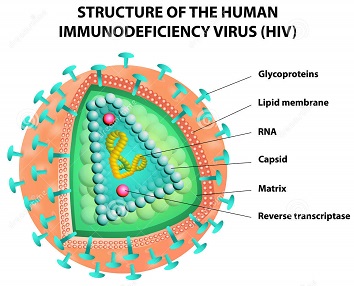 |
Viruses are not like cells. They are protein and membrance packages that
carry RNA instead of DNA and have few working parts. Viruses use host
cells to reproduce by attaching themselves, injecting their own RNA and
taking over the host cell. The host cell burst when hundreds or thousands
of viruses have been made and are ready to take over other cells. Viruses do not eat or grow, so are often not considered as living things by definition. |
|
Modeling Some Types of models that are used to represent ideas and systems are:
|
|
|
Investigation |
|
| Scientist Robert Hooke |
|
| |
Technology Microscopes: |