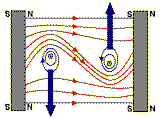
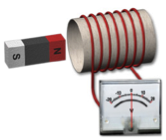
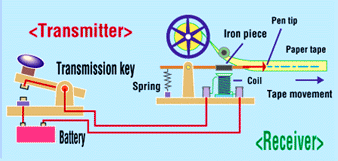
| Picture |
Core Knowledge or Concept
|
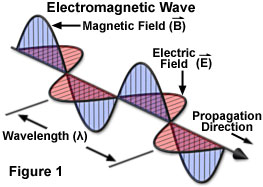
|
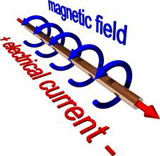
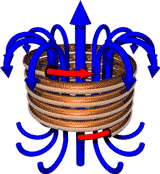
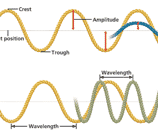
Electromagnetic waves carry both electrical and magnetic energy.
In a vacuum (outer space), they travel at the
speed of light, 300,000km / second.
Electromagnetic radiation
is the energy transferred by electromagnetic waves.
|
 |
Wave Model of Electromagnetic Waves (Light)
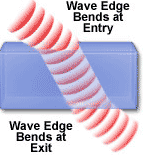
EM waves act like transverse waves. By using
polarized filters or lenses, waves that are vibrating in certain
directions can be blocked like a rope waved through a picket fence.
|
|
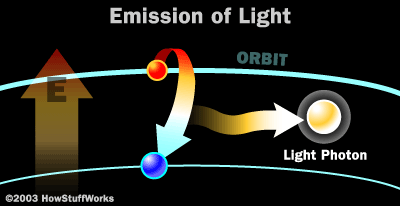
Particle Model of Electromagnetic Waves (Light)
A photon a tiny packet of
light that acts as both a wave and a particle.
They are created when electrons lose energy or when protons fuse in the
sun.
They can create electricity when they hit electrons in solar panels.
|

|
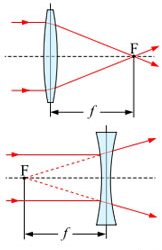
A
ray is a straight line used to
represent a light wave in diagrams and in mathematics.
|

|
The electromagnetic
spectrum
is the entire range of frequencies and wavelengths of electromagnetic
waves including the visible spectrum that we see as colors. (i.e. radio
waves, microwave, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma
rays.)
|

|
Radio Waves:
Long waves with low energy, these are used in AM/FM radios, HAM and
short-wave radios, walky-talkies, baby monitors, and the like.
|

|
Microwaves:
Shorter radio waves are called microwaves. Water in microwave ovens
responds to these frequencies by vibrating and heating up.
Radar
systems and some communication devices use these frequencies.
|

|
Infrared waves
Just below the visible spectrum is infrared light. It is given off by
everything that radiates heat.
Thermograms
can pick up these heat rays, giving us a way to see in the dark using
cameras that convert infrared to visible light.
|

|
Visible Light
Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet and all shades between.
These are the frequencies that our eyes can see.
|

|
Ultraviolet Rays
High frequency light waves that bees and other insects can see, but humans
can not. Skin responds by darkening (tans) and making vitamin D.
Ultraviolet light can kill or mutate cells by breaking DNA and causing
mutations.
|
|
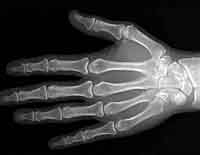
X-Rays
High energy rays that can penetrate soft tissues, leaving white spots on
film where they were blocked by bone or other dense things.
Engineers use them to find cracks in metals and cement structures.
|
|
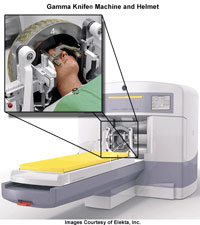
Gamma Rays
The most energy with the shortest wavelength & highest frequency.
They are the only rays strong enough to escape some stars in large bursts.
Used in medicine to kill tumors using tools like the gamma knife (left) |

|
Scientist
Karl G. Jansky
(1905-1950) Bell Laboratories Engineer Invented
Radio Astronomy
when he was looking for sources of static that could interfere with the
newly invented radio broadcast systems. He concluded that the biggest
source of radiation was coming from the Mily Way galaxy.
|
|
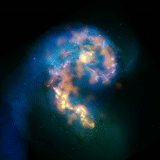
Technology
Radio
Telescopes: The Atacama
Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array "ALMA's test views of the
Antennae show us star-forming regions on a level of detail that no other
telescope on Earth or in space has attained. This capability can only get
much better as ALMA nears completion," said Dr. Mark McKinnon, North
American ALMA Project Manager from the NRAO in Charlottesville, Virginia.
|















































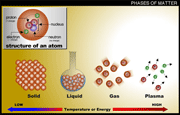








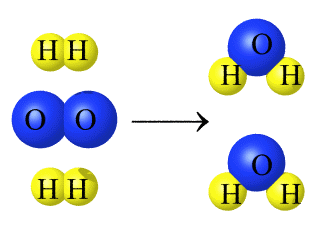
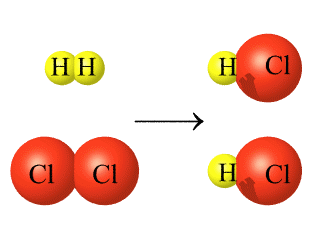


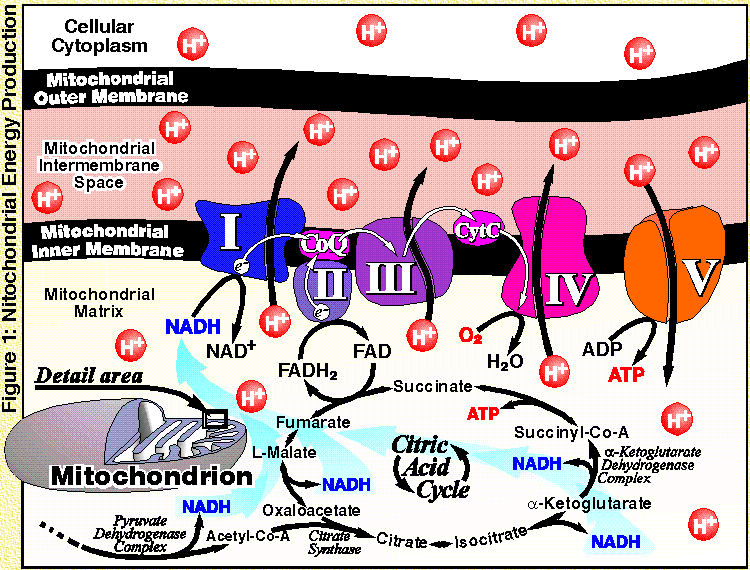




























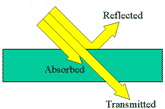

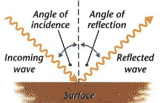
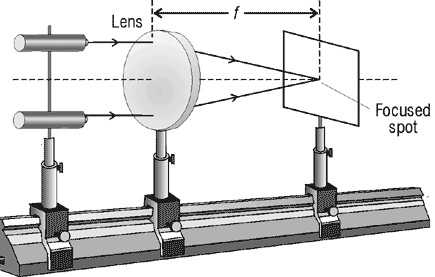
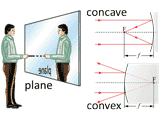


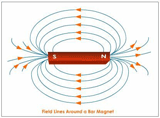
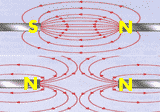
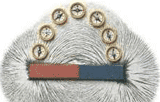
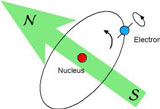
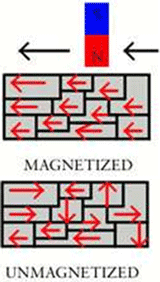

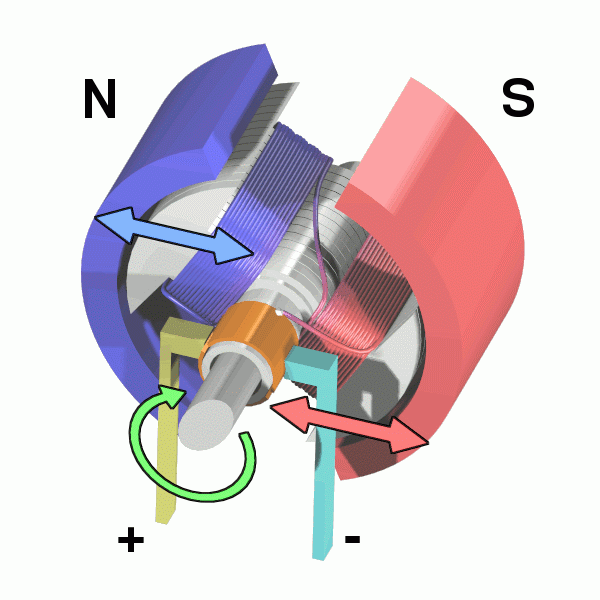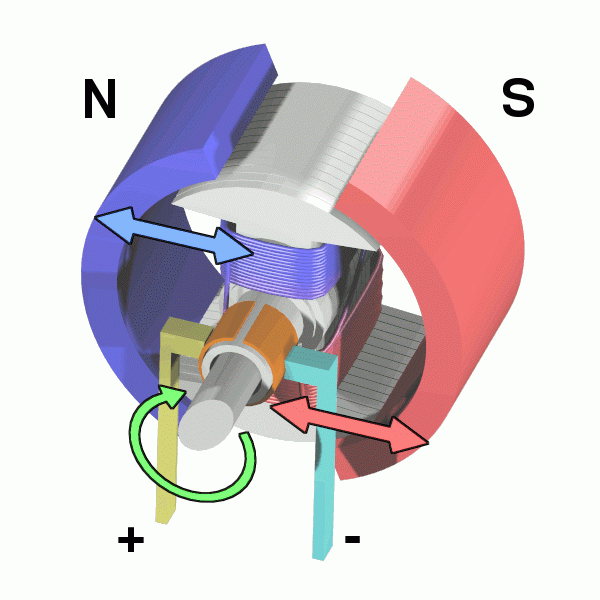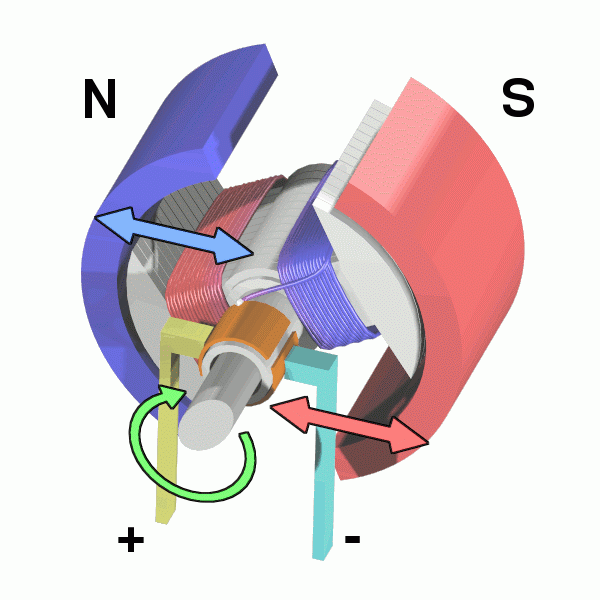
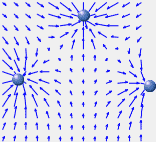
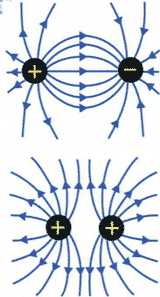




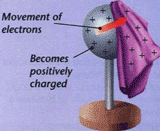
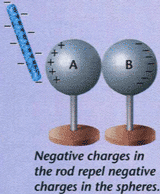
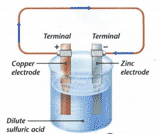

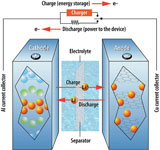
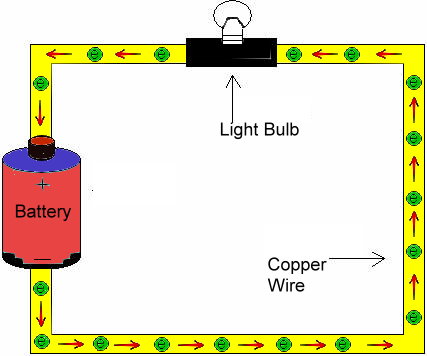
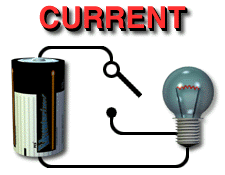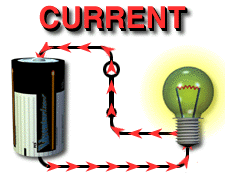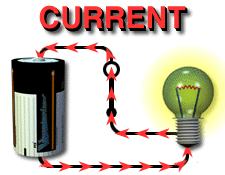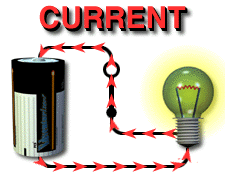

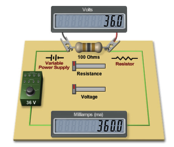
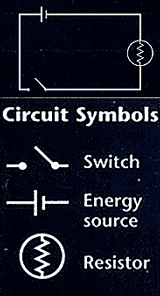
 The
relationship between resistance, voltage, and current is summed up in
The
relationship between resistance, voltage, and current is summed up in